The board of directors plays a crucial role in corporate governance, making important decisions that shape an organization’s path. Central to the success of this role is the adherence to ethical behavior, which serves as the foundation for maintaining good corporate governance. However, there are instances when boards deviate from these ethical standards, engaging in practices that undermine their responsibilities and compromise the interests of stakeholders.
In this article, we will explore five examples of inappropriate board member behavior, examining the consequences and implications of such actions.
Common Unethical Practices Your Board Should Avoid
1. Financial Fraud

Financial fraud refers to deceptive practices or intentional misrepresentation of financial information — deliberately deceiving stakeholders. When board members engage in financial fraud, they manipulate financial statements, inflate revenues, understate expenses, or hide liabilities. These actions can mislead investors, creditors, employees, and the public about the company’s true financial health.
A real case of financial fraud: In 2022, Danske Bank, the largest bank in Denmark, pleaded guilty and agreed to forfeit $2 billion to resolve an investigation by the United States into its fraudulent activities involving US banks. The bank was found to have manipulated anti-money laundering controls, allowing high-risk customers, including those in Russia, to access the US financial system.
What are its consequences and legal implications?
The impact of financial fraud on stakeholders is substantial. Investors may suffer significant financial losses when they make decisions based on fraudulent information. Creditors might face difficulties in recovering their loans, and employees may experience job insecurity if the fraud leads to financial instability or bankruptcy. Moreover, financial fraud undermines the trust and confidence of stakeholders in the company and the overall market.
Financial fraud also carries severe legal implications. It violates various laws and regulations, such as securities fraud, accounting fraud, and false statements to auditors. Board members involved in financial fraud may face criminal charges, fines, civil lawsuits, and even imprisonment. The consequences can extend beyond the individual board members to the entire organization, leading to reputational damage and loss of market value.
What’s the role of the board in preventing financial fraud?
Board members have ethical responsibilities to prevent and detect financial fraud. They should establish a strong ethical culture, promote transparency, and ensure the implementation of robust internal controls. This includes establishing an effective system of checks and balances, conducting regular audits, and providing proper oversight of financial reporting processes. By fulfilling their ethical duties, board members can protect stakeholders’ interests and maintain the integrity of the organization.
2. Insider Trading
Insider trading occurs when board members trade stocks or other securities of their company based on non-public, material information. This unethical practice undermines market integrity and investor confidence. By doing insider trading, board members gain an unfair advantage over other investors.
A real case of insider trading: Nine individuals, including a former US congressman from Indiana, tech company executives, an investment banker, and a man training to be an FBI agent, have been charged in four separate insider trading schemes last 2022.
The indictments, unsealed in New York City, mark one of the most significant crackdowns on insider trading in a decade. The defendants allegedly made millions of dollars in illegal profits through trading on nonpublic information. Authorities have vowed to continue pursuing similar prosecutions in the future.
What are its ethical and legal ramifications?
Ethically, insider trading violates the principle of fairness and undermines the trust and integrity of financial markets. It gives an unfair advantage to individuals who possess non-public, material information — enabling them to make trades that exploit others’ lack of information.
Insider trading is prohibited by securities laws in most jurisdictions, making it illegal. Those who engage in insider trading can face substantial fines, imprisonment, the requirement to return ill-gotten profits, and potential civil lawsuits.
Regulatory bodies, such as the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), enforce strict measures to detect and punish insider trading. These measures include monitoring trading patterns, conducting investigations, and imposing penalties to deter such practices.
How can the board of directors prevent insider trading?
To prevent insider trading, board members must adhere to ethical and legal standards. They should maintain strict confidentiality and avoid trading on material non-public information. Establishing clear policies and procedures that prohibit insider trading, along with educating board members about their obligations, is essential. Regular training and oversight can help ensure compliance and foster a culture of integrity within the organization.
3. Bribery and Corruption
Bribery and corruption involve the offering, giving, receiving, or soliciting of improper inducements — money, gifts, or favors — to influence business decisions or gain an unfair advantage. It encompasses actions that compromise the integrity of organizations.
A real case of bribery and corruption: Swedish telecom equipment maker Ericsson agreed to plead guilty to US foreign corruption violations and pay over $206 million for breaking a previous agreement with the Justice Department. The charges involve bribery and falsifying records in countries such as China and Kuwait.
Ericsson used intermediaries to bribe officials and mishandled cash transactions. The company’s failure to provide the required documents and information resulted in the breach. Ericsson faces penalties and probation, and will retain an independent compliance monitor.
What are the reputational impact and legal ramifications?
This unethical behavior of board of directors can erode trust and cause harm to an organization’s reputation. When board members engage in these unethical practices, they compromise fair competition, distort business decisions, and erode trust within the organization. A damaged reputation hampers the organization’s ability to attract and retain clients, partners, and investors.
If found guilty, boards may face substantial fines, penalties, and even imprisonment. Organizations can also be held responsible for their employees’ actions. This may lead to financial penalties, the need to return illegal profits, and legal constraints on operations.
What’s the role of the board in enforcing anti-bribery and corruption policies?
Promoting transparency and ethical behavior is a crucial responsibility of boards. To prevent bribery and corruption, they can implement robust internal controls, conduct thorough due diligence on business partners, and offer anti-corruption training. These measures are beneficial for detecting unethical practices, thus maintaining a culture of high ethical standards.
4. Conflict of Interest
Conflict of interest occurs when the board’s personal or financial interests impact their decision-making. This ethical concern arises when directors place self-interest above the organization and stakeholders’ interests. Conflict of interest undermines impartiality, compromising the board’s ability to make well-rounded decisions.
A real case of conflict of interest: In recent news, US Supreme Court Justice Clarence Thomas is facing conflict of interest accusations due to his relationship with billionaire Harlan Crow. It has been revealed that Thomas traveled with Crow to Indonesia for nine days in 2019, with the expenses covered by Crow.
Thomas has also been a regular passenger on Crow’s private jet for two decades. Crow paid for a year of schooling for Thomas’ grandnephew in Georgia. These revelations raise concerns about impartiality and ethical considerations.
What are its consequences and legal implications?
Neglecting conflicts of interest can lead to significant repercussions, such as reputational damage and erosion of public trust. Shareholder activism may also occur should shareholders doubt the fairness of board decisions. From a legal standpoint, regulatory investigations, criminal charges, and financial penalties can be imposed.
What are the obligations of the board in managing conflicts of interest?
Board members have the responsibility to disclose and manage conflicts of interest transparently. They can opt to implement strict procedures such as abstaining from discussions and votes on conflicted matters. This way, boards can prevent bias, protect the integrity of the board’s actions, and uphold ethical standards.
5. Failure to Protect Stakeholder Interests
Board members have fiduciary responsibilities to act in the best interests of stakeholders. However, instances occur where they prioritize personal interests or fail to fulfill their duties — resulting in breaches of trust and ethical misconduct.
This unethical practice can manifest in various forms, such as:
- making decisions that solely benefit a select few
- neglecting stakeholder concerns
- disregarding ethical considerations
- engaging in actions that harm the stakeholders’ overall welfare.
What are its consequences and legal implications?
When board members neglect their fiduciary responsibilities, legal actions can be initiated. These may include shareholder lawsuits, regulatory investigations, and enforcement actions. This can result in financial penalties, reputational damage, and potential removal of board members.
Moreover, the organization may experience a loss of trust, diminished investor confidence, and decreased market value — impacting its ability to attract investments and sustain long-term success. Fulfilling fiduciary responsibilities helps avoid such consequences and maintain stakeholder trust.
Frequently Asked Questions about Board of Directors’ Misconduct

Corporate boards are expected to have a proactive approach to deter misconduct. On the other hand, it’s vital to still have the right reactive responses in case the board of directors’ misconduct is detected. Make your board more well-informed with these frequently asked questions:
1. What to do about a toxic board of directors?
If you suspect a toxic board of directors, consider the following actions:
- Document concerns: Keep a record of specific instances of toxic behavior or decisions made by the board.
- Engage with other shareholders: Communicate with other shareholders to build a consensus on the issues and potential solutions.
- Advocate for change: Use your voting power during annual meetings to elect new directors who align with ethical and responsible governance principles.
- Seek legal advice: Consult with legal experts to explore any legal avenues available to address the situation.
2. What are the signs of a dysfunctional board of directors?
Signs of a dysfunctional board of directors may include:
- Lack of open communication and transparency among board members.
- Frequent conflicts and disagreements within the board that hinder decision-making.
- Absence of constructive criticism or challenging questions during board meetings.
- Overly dominant board leadership that suppresses opposing viewpoints.
- Inadequate diversity among board members in terms of skills, experience, or background.
- Failure to hold management accountable for poor performance or unethical behavior.
- Disregard for shareholder concerns and interests.
- High turnover of board members due to resignations or disagreements.
3. What is an example of conflict between the board and management?
One example is related to executive compensation. The board is responsible for setting executive compensation packages, including salaries, bonuses, stock options, and other benefits. If the management believes they deserve higher compensation than what the board approves, conflicts may arise.
For instance, the management might argue that their performance justifies higher compensation, while the board may consider the proposed packages excessive and not aligned with company performance. This conflict can lead to tension between the board and management, impacting decision-making and overall corporate governance.
4. How can shareholders play a role in preventing board corporate misconduct?
Shareholders have an important role in preventing board corporate misconduct. Some actions they can take include:
- Active engagement: Attending annual general meetings, asking questions, and voicing concerns about governance practices can help hold the board accountable.
- Proxy voting: Utilizing proxy voting rights to elect directors who prioritize ethical conduct and responsible governance can influence board composition and decision-making.
- Shareholder resolutions: Submitting shareholder resolutions on specific governance matters can raise awareness, initiate discussions, and push for changes in board practices.
- Shareholder activism: Activist shareholders can use their influence to advocate for changes in board leadership, governance structures, or strategic decisions to ensure ethical corporate behavior.
- Collaborative initiatives: Joining or supporting shareholder advocacy groups and initiatives focused on responsible corporate governance can amplify shareholder voices and bring about systemic change.
The effectiveness of these actions may vary depending on the specific circumstances and legal frameworks in different jurisdictions.
5. How can corporate governance mechanisms prevent board corporate misconduct?
Corporate governance mechanisms play a crucial role in preventing board corporate misconduct. Some key mechanisms include:
- Independent board members: Having independent directors who are not affiliated with the company or its management can bring objectivity and provide checks and balances to prevent misconduct.
- Board diversity: A diverse board, including members with varied backgrounds, experiences, and perspectives, can foster robust discussions, reduce groupthink, and enhance accountability.
- Effective board committees: Committees such as the audit committee and ethics committee can oversee financial reporting, internal controls, and ethical compliance, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Board evaluations: Regular evaluations of board performance can identify weaknesses or conflicts of interest, enabling corrective actions and enhancing board effectiveness.
- Whistleblower protection: Establishing mechanisms to encourage employees and stakeholders to report potential misconduct without fear of retaliation promotes early detection and prevention of unethical behavior.
Convene: Helping You Deter Unethical Practices the Simple Way
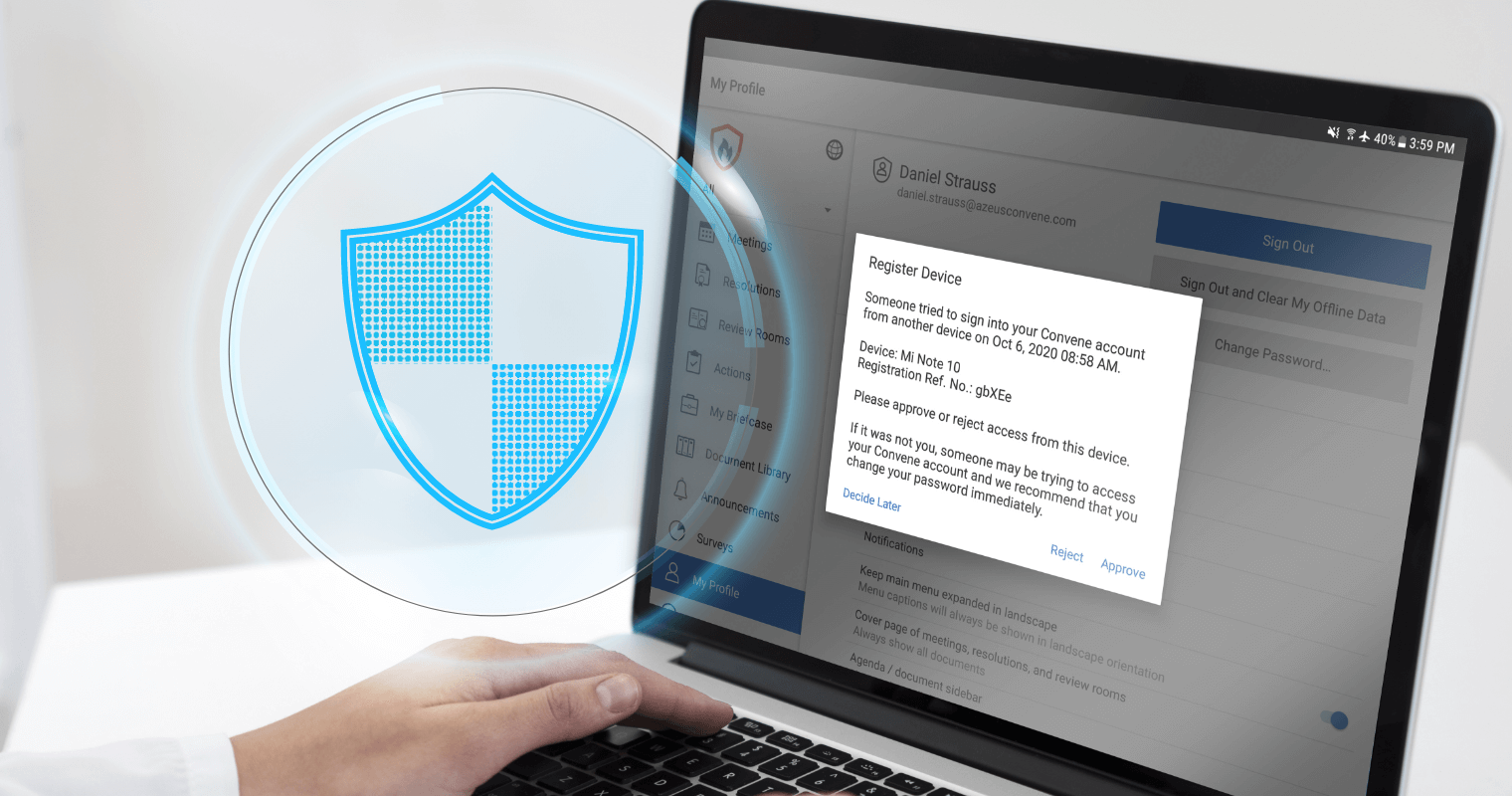
Unethical practices have far-reaching consequences for boards, which may lead to legal ramifications, reputational damage, and loss of trust. For boards that want to prevent and manage such practices, using board portals like Convene is an ideal solution.
Convene offers secure and encrypted communication tools for the exchange of confidential information and sensitive matters, preventing unauthorized access. It can also enhance board oversight by offering features such as real-time voting, task assignment, and performance evaluations. These functionalities promote accountability and enable directors to monitor and evaluate each other’s actions and adherence to ethical standards.
In addition, Convene provides an audit trail feature and robust meeting tools. Users can access a traceable record of board activities and decisions — from document version history to voting results — promoting transparency. Boards can also streamline their meetings by organizing agendas, documents, and minutes in a centralized platform. With Convene, boards can improve their efficiency and maintain the highest standards of transparency and integrity.
Mitigate the risk of unethical behavior with Convene today. Book a demo now!
Jielynne is a Content Marketing Writer at Convene. With over six years of professional writing experience, she has worked with several SEO and digital marketing agencies, both local and international. She strives in crafting clear marketing copies and creative content for various platforms of Convene, such as the website and social media. Jielynne displays a decided lack of knowledge about football and calculus, but proudly aces in literary arts and corporate governance.