The demand for cloud technology is skyrocketing across industries as businesses transition their operations to digital. Research says that 85% of organizations are preparing for a “cloud-first” approach by 2025 to drive digital transformation. In healthcare alone, experts estimate that the total global spending for cloud technology will exceed 89 billion USD. This solidifies the significant impact of cloud-based services in boosting overall efficiency.
Is your health organization maximizing the potential of cloud computing? Explore in this article the cloud computing healthcare benefits, its potential risks and challenges, and discover the best practices for implementing this technology.
What is cloud computing in healthcare industry?
Healthcare providers utilize cloud computing for storing, managing, and processing medical-related data and applications. Unlike traditional IT infrastructures that are physically installed, cloud computing uses remote servers hosted via the Internet. This setup allows users to access data from anywhere, reducing on-site infrastructure costs and enhancing collaboration among medical professionals.
Healthcare cloud services make sharing medical records smoother, safer, and faster between parties. Effective for streamlining workflows, it lessens human errors by automating backend operations. The technology has also proven its importance for creating and maintaining telehealth applications and software for hospitals, research centers, and military operations. Ultimately, this improves patient care and accessibility to medical services.
Real-World Applications of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
The impact of cloud computing on healthcare is evident in various areas such as telemedicine, electronic health records (EHRs), and drug development. Organizations use these cloud solutions in the following capacities:
Telemedicine applications enable doctors to monitor and treat patients remotely via video consultations.
- Cloud-based medical research tools leverage cloud computing to simulate chemical reactions by developing virtual models of molecules and formulas for drug development.
- Information Management System (IMS) empowers medical personnel to store, manage, and share medical records secured with granular access controls.
- Digital Libraries and Shared Knowledge Databases are cloud-powered repositories where healthcare organizations and professionals can access the latest medical research and clinical standards.
- Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS) assists healthcare providers in analyzing patient data to recommend evidence-based treatments, facilitating data-driven decision-making.
- Virtual Education platforms are online spaces for facilitating remote learning through interactive modules, case studies, and virtual labs.
- Healthcare Appointment Management System streamlines appointment scheduling, improving efficiency in patient care and reducing administrative burden.
- Digital Rights Management System protects sensitive healthcare content by managing user permission on digital assets to ensure compliance with privacy regulations.
- Population Health Research and Modelling tools enable researchers to process large-scale data important when creating model trends, identifying risks, and developing preventive measures.
What are the benefits of cloud computing in healthcare?
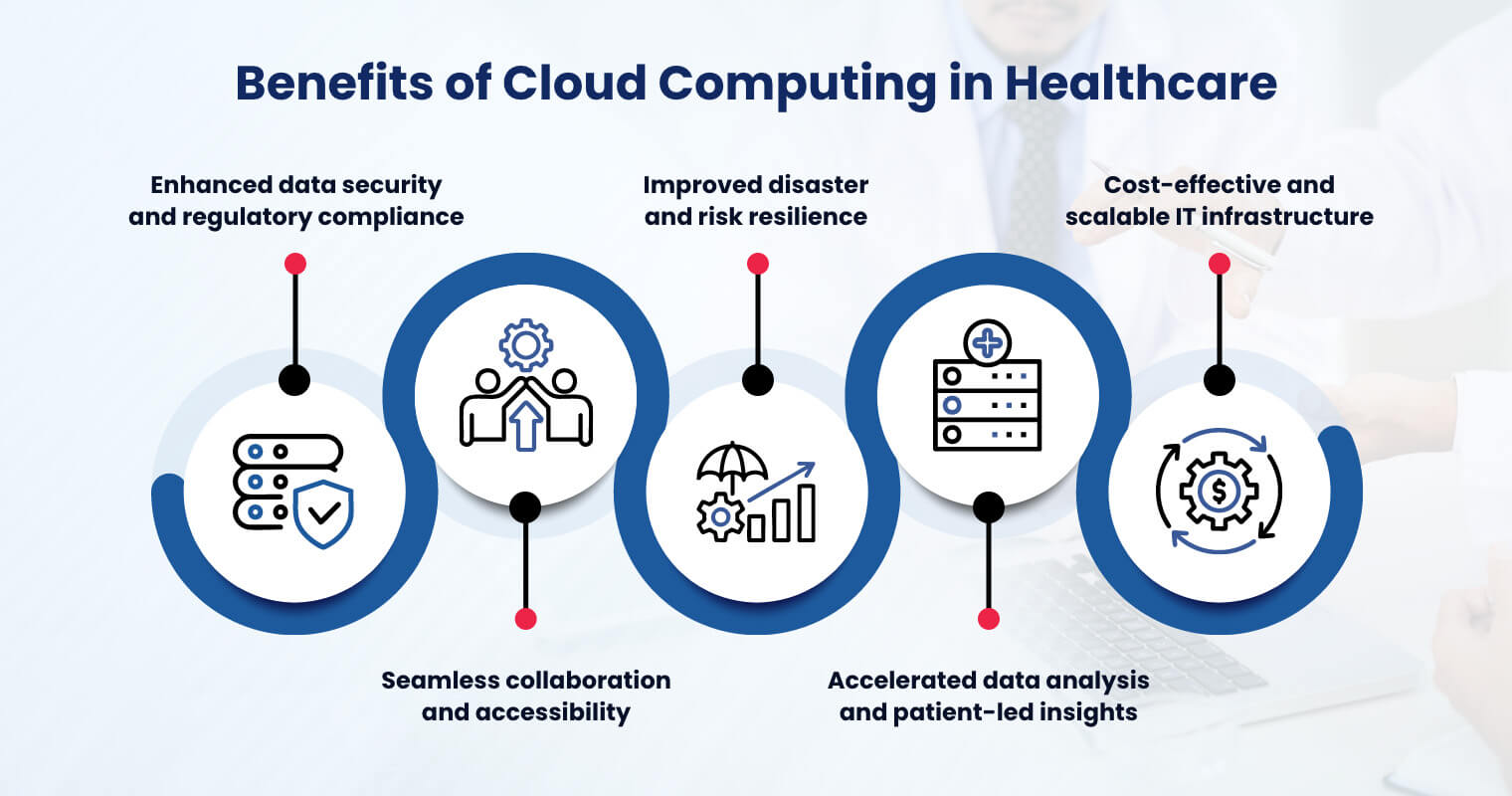
The impact of healthcare cloud computing extends to providers and patients. Among cloud computing healthcare benefits, here are the top advantages you can expect after the transition.
1. Enhanced data security and regulatory compliance
The evolving nature of cybersecurity threats urges healthcare providers to prioritize data security. Aiding to protect sensitive data, cloud technology in healthcare provides robust security features like data encryption and access controls, significantly mitigating the risks of data breaches and leaks.
These cloud-based infrastructures are pre-configured to comply with regulatory standards, simplifying the work of healthcare compliance officers when adhering to local, state, and global standards such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of the United States and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) of the European Union.
2. Seamless collaboration and accessibility
Cloud solutions facilitate efficient and secure information sharing by centralizing medical data in a single, accessible space. It enhances coordination between doctors, nurses, and staff speeding up services and updates. Streamlining experiences with applications and software, cloud computing is vital to elevating patient care and satisfaction.
3. Improved disaster and risk resilience
Storing data on a cloud-hosted platform contributes to more resilient IT infrastructures. It uses redundancy and automatic backups capable of preserving data even if local systems fail. In an industry where real-time access to records is critical, cloud computing is an effective disaster recovery strategy that can minimize the impact of natural or human-made disruptions.
4. Accelerated data analysis and patient-led insights
Data analysis is a core practice in the healthcare industry. This function drives innovation, clinical decisions, and operational optimizations. With the massive amounts of data generated—from patient records, medical images, clinical trials, and operational metrics—cloud technology equips healthcare professionals with advanced tools to process and analyze datasets faster. This uncovers patterns and trends in patient data that healthcare providers can evaluate to address gaps more effectively.
5. Cost-effective and scalable IT infrastructure
Investing in digital solutions such as healthcare cloud technology is a cost-effective and sustainable decision due to its scalability. It eliminates the need for physical IT infrastructures, lessening the expenses for on-the-ground maintenance. Cloud services for healthcare are also customizable with provisions for future downscaling or upscaling, making the transition to cloud technology more economical as operations evolve.
Types of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
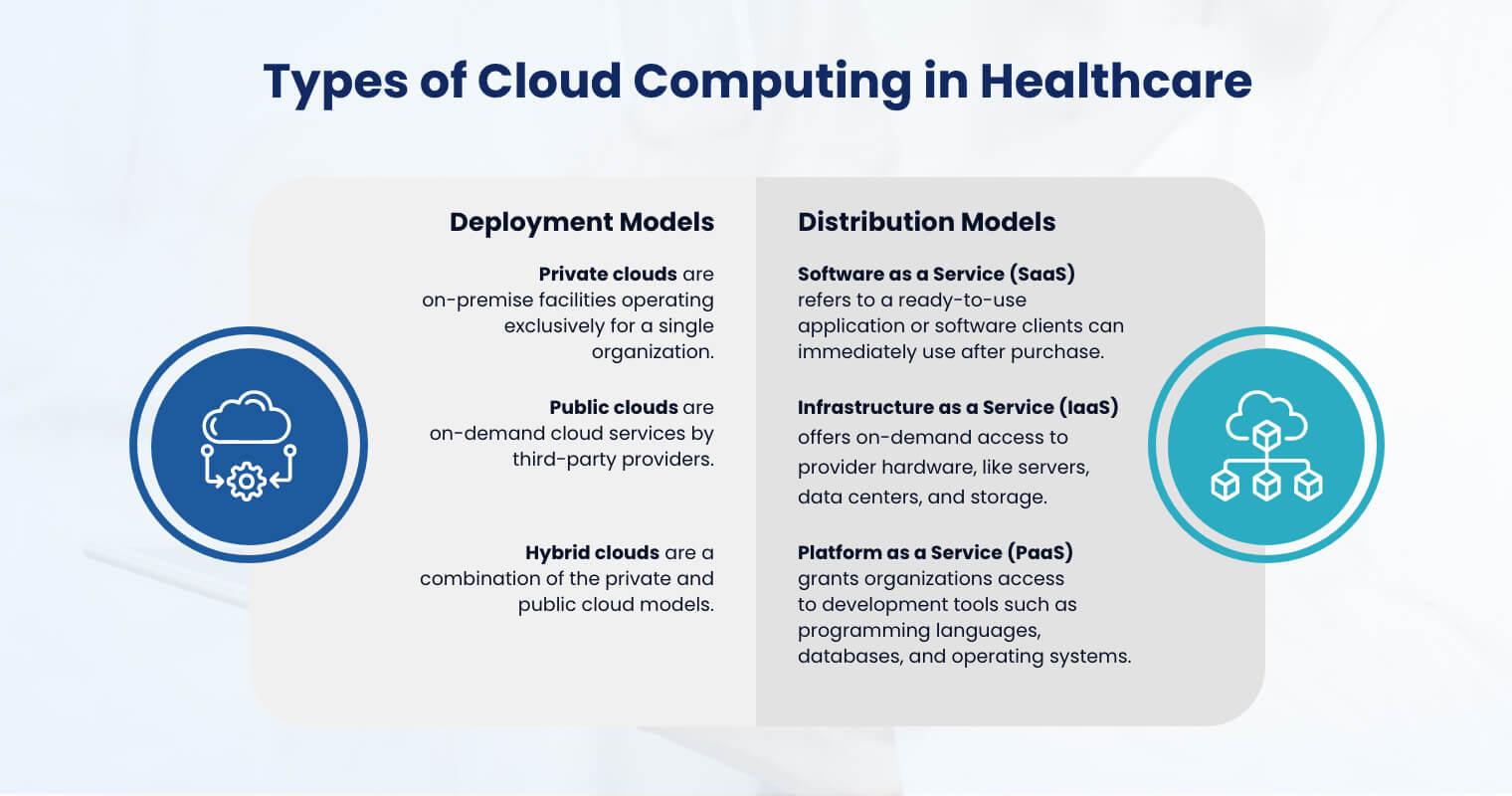
Cloud computing in healthcare is categorized into two key models: deployment and distribution. Both offer distinct approaches, allowing healthcare providers to tailor solutions to their unique needs.
Deployment Models
There are three types of deployment models organizations can choose from when adopting cloud technology.
- Private clouds are on-premise facilities operating exclusively for a single organization. This is ideal for those with funds to manage a dedicated infrastructure, ensuring high-level security over sensitive healthcare data and applications.
- Public clouds are on-demand cloud services by third-party providers. Shared by multiple clients, public clouds don’t require maintenance expenses, making them a cost-effective solution for businesses of all sizes. This is for those wanting to focus on their core operations rather than IT infrastructures. Well-known examples of third-party cloud service providers are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), IMB, Microsoft Azure, Oracle, and Tencent Cloud.
- Hybrid clouds are a combination of the private and public cloud models. It presents a more flexible and scalable cloud solution, allowing clients to create a unified environment that leverages public clouds for workload bursts and private clouds for sensitive data and applications.
Unsure which cloud hosting option best suits your organization? Here’s a whitepaper offering valuable insights to support your decision-making process.
Guide to Selecting the Right Hosting Option
Distribution Models
Cloud distribution in healthcare comes in varying levels of services depending on the needs of an organization.
- Software as a Service (SaaS) refers to a ready-to-use application or software clients can immediately use after purchase. The maintenance of this lies with the developer and requires minimal client effort.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides on-request access to the hardware facilities of the provider, including servers, data centers, and storage clusters. This approach fits organizations that want to deploy their proprietary system while saving on IT infrastructure costs.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) grants organizations access to development tools such as programming languages, databases, and operating systems. It allows them to create and deploy specific software independently with read-to-use modules.
What are the risks of storing healthcare data in the cloud?
Embracing cloud technology also comes with significant risks healthcare providers must understand before transitioning. Discover the potential pitfalls of storing medical data in the cloud.
1. Data privacy and ownership concerns
Adopting cloud computing in the healthcare industry presents complex challenges related to data privacy and ownership due to the sensitive information it generates. Third-party providers operate their public and hybrid clouds across various locations, making it difficult for clients to control their data. If situations where cloud providers mishandle or fail to protect data, it can cause privacy law violations and reputational damage.
2. Interoperability and integration bottlenecks
Transitions from legacy technologies to cloud solutions for healthcare industry typically cause integration issues. When a chosen cloud system is incompatible with the existing system, it hinders data exchange and disrupts workflows. Additionally, it can affect coordination among hospitals, specialists, and clinics, slowing down decisions and compromising patient services. To successfully integrate the cloud, healthcare providers must practice standardization across data and select a cloud solution compatible with their existing systems.
3. Consistent regulatory compliance
Healthcare providers should strategically plan how to maintain compliance when adopting cloud solutions. They can face serious risks if they fail to align their cloud practices with the latest regulatory frameworks. Choosing a provider committed to complying with evolving regulatory frameworks will help strengthen an organization’s data governance practices and reputation.
4. Optimizing resource allocation
Healthcare providers must strike a balance between cost efficiency, data security, and operational needs when selecting a cloud provider. Over- or underestimating resources and requirements can lead to inefficiencies such as wasted resources or limited storage and operability. Make prudent decisions by carefully evaluating objectives and specific requirements, including the number of users, data security needs, and anticipated workloads.
5. Cybersecurity threats
There’s a higher risk of cybersecurity for healthcare providers storing data in the cloud. In the United States, healthcare institutions have so far reported 386 healthcare attacks in 2024. These frequent attacks of hackers on hospitals and clinics are due to the sensitive nature of patient data and its high value in the black market, often exchanged for high sums of money. Healthcare providers can mitigate cybersecurity threats and avoid their damages with robust backup and recovery procedures, regular patch tests for vulnerabilities, and staff training for security awareness.
6. Outages and downtimes
No system is completely immune to outages, even cloud storage with high availability and uptime guarantees. Downtimes can jeopardize the operations of healthcare providers, leading to delays in patient care and access to critical data. Additionally, prolonged outages can cause serious financial and credibility loss, impacting the provider’s reputation. Ensure you partner with a cloud provider with solid business continuity plans to minimize operational disruption during sudden downtimes.
Best Practices for Secure and Compliant Cloud Usage in Healthcare
Security and compliance must be a priority when migrating to or expanding their cloud infrastructures. Here are the top best practices to ensure seamless and successful cloud usage.
1. Outline your requirements
Start by understanding your organization’s needs and objectives. Prioritize which data are most critical to migrate and ensure compliance with relevant regulations. Before talking with cloud service providers, tailor your requirements further by discussing budget allocation and cloud data management requirements with the board of directors.
2. Conduct thorough vendor evaluation
When assessing potential vendors, remember it’s important to evaluate their current performance and long-term strategy for adapting to shifting regulatory and technological trends. This will reveal competitive vendors capable of meeting your immediate and growing requirements.
Other key considerations include:
- Experience and expertise in serving healthcare providers
- Customer service and support for implementation and post-deployment
- Compliance with regulatory standards
- Guidelines on cloud security in healthcare
- Scalability
- Vendor lock-in terms
3. Implement robust data encryption and access controls
Discuss with the provider your standards for data handling by establishing protocols for data encryption (in transit and while at rest), granular access controls, data loss prevention, and multi-factor authentication.
4. Perform regular audits
Maintain a high level of security at all times by conducting regular monitoring of infrastructure settings, access logs, and activities. Assemble a team to run security assessments and vulnerability scans to pinpoint threats.
To ensure business continuity, establish incident response and disaster recovery plans. These will guide you to effectively navigate unforeseen occurrences such as security breaches, data loss, and system failures. Consider storing backups in diverse locations and testing these processes regularly to ensure their reliability, minimizing downtime and data loss.
5. Provide security training
Cloud-based systems must evolve with regulatory requirements and technology. Ongoing staff training is essential to keep pace with these changes. By conducting regular cybersecurity awareness training, healthcare providers can mitigate risks caused by human errors, especially on technical topics such as phishing prevention, secure file sharing, and data access protocols.
Convene as a Cloud-Hosted Board Portal Software
Businesses view digitalization as a need to remain competitive. Convene is leading the way with cloud-hosted board portal software specializing in streamlining and enhancing the operations of modern-day boards.
Harnessing cloud technology, Convene is a digital solution that provides organizations with a secure, scalable, and accessible platform that empowers leaders in strategic decision-making.
Convene’s environments are fortified with the following state-of-the-art security measures.
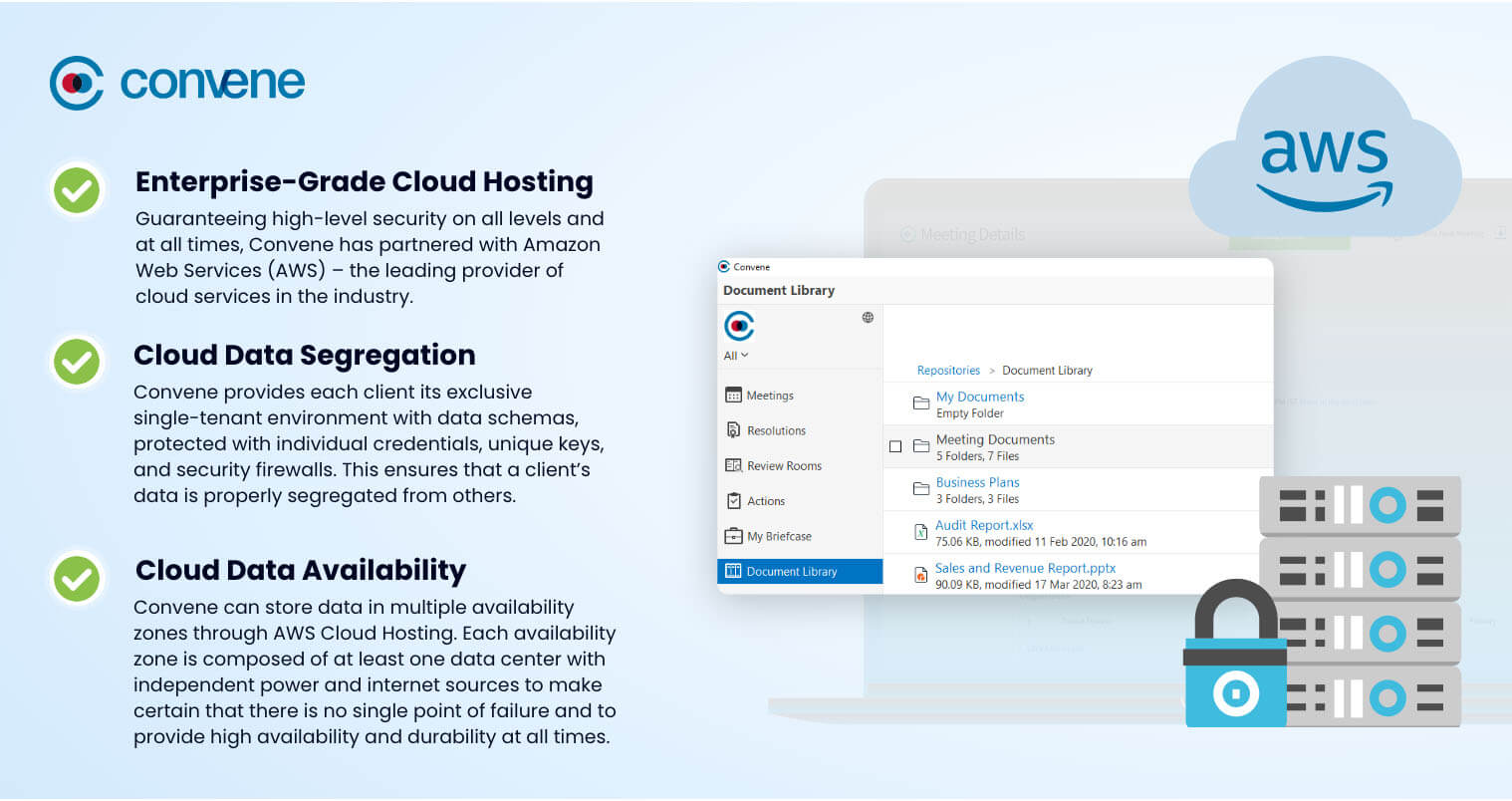
Enterprise-Grade Cloud Hosting
Guaranteeing high-level security on all levels and at all times, Convene has partnered with Amazon Web Services (AWS) – the leading provider of cloud services in the industry.
Cloud Data Segregation
Convene provides each client its exclusive single-tenant environment with data schemas, protected with individual credentials, unique keys, and security firewalls. This ensures that a client’s data is properly segregated from others.
Cloud Data Availability
Convene can store data in multiple availability zones through AWS Cloud Hosting. Each availability zone is composed of at least one data center with independent power and internet sources to make certain that there is no single point of failure and to provide high availability and durability at all times.
Enhancing Healthcare Security and Compliance with Convene
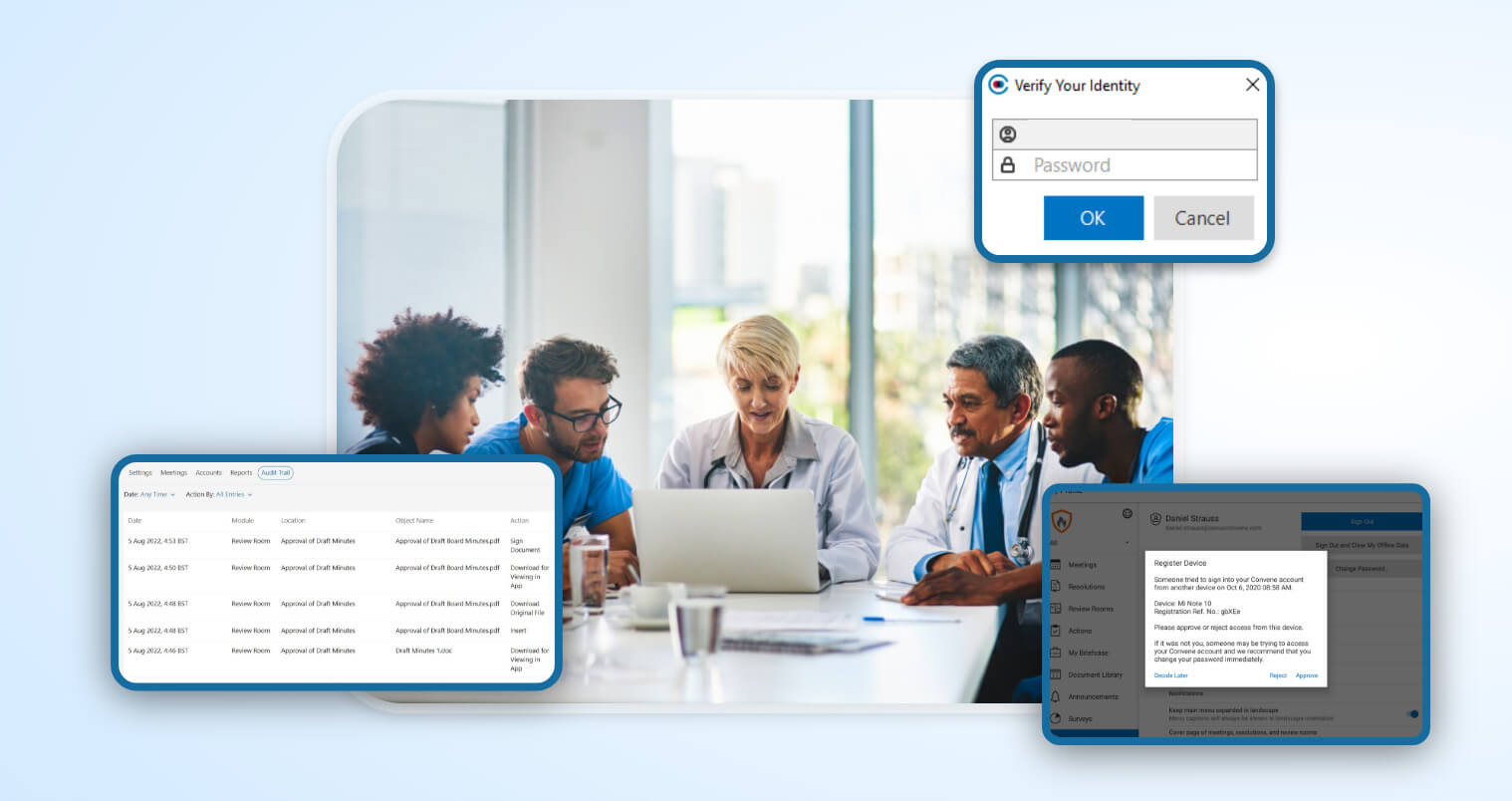
- Convene is a HIPAA-certified board management software that provides a secure and compliant platform for managing board operations, ensuring a seamless transition to digital workflows.
- The platform grants clients full system ownership, allowing them to configure user roles and device settings based on their preferences.
- Convene employs robust security protocols across devices so users can access the app via mobile, tablet, or desktop without worrying about breaches and leaks.
- The Convene cloud infrastructure is protected with an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) that scans traffic and blocks suspicious activity, including uploads containing malware.
- The platform conducts daily automated backups to ensure data integrity, while unused or obsolete archives are destroyed and replaced to prevent unauthorized retrieval.
Ready to learn more? Book a Convene demo today to see how our cloud-based board management software can revolutionize your healthcare practice.
Jean is a Content Marketing Specialist at Convene, with over four years of experience driving brand authority and influence growth through effective B2B content strategies. Eager to deliver impactful results, Jean is a data-driven marketer who combines creativity with analytics. In her downtime, Jean relaxes by watching documentaries and mystery thrillers.