Formed in 1981, the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) is known for its vast oil reserves, dynamic economies, and high quality of life. Capitalising on these strategic advantages, the Gulf nations consistently innovate their systems to enhance business processes and encourage foreign and domestic investments. Central to this effort are regulatory compliance frameworks that ensure transparency and accountability as regional and global markets evolve.
For businesses to thrive in such a competitive region, it is crucial to understand the various regulations surrounding it. This article explores the state of regulatory compliance in the UAE and GCC nations, providing insights into their frameworks and key initiatives shaping regulatory environments.
State of Regulatory Compliance in UAE and GCC Nations
Regulations are sets of rules and standards by policymakers to ensure compliance and transparency among corporations, nonprofits, and government entities. Typically presented as frameworks, these regulations serve as governance tools to drive economic development and promote accountability, public safety, and social equity.
The GCC is a long-standing regional and economic alliance in the Arabian Peninsula, composed of six member states, namely the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, and Saudi Arabia. In recent years, the Gulf nations have been driving collective efforts to digitise governance systems and diversify away from oil.
The UAE stands out among the Gulf nations for successfully utilising regulatory compliance to build influential business hubs, such as Dubai and Abu Dhabi. Before delving into the UAE’s various regulatory frameworks, learn about its different jurisdictions to understand how this approach influences its business climate.
- Financial Free Zones (FFZs) are specialised economic zones developed to attract foreign markets. As of 2024, 46 free zones operate in the UAE, each with dedicated regulators. Well-known examples of these zones are the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) and the Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM).
- Mainland UAE refers to areas outside FFZs where federal laws and UAE regulations apply. These locations primarily serve local markets, where businesses can expand within and outside the country.
In line with the GCC’s objective of economic diversification, other Gulf nations are also completing national initiatives to reshape their regulatory landscapes. Among these are Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030, Bahrain’s Economic Vision 2030, Oman’s Vision 2040, Qatar’s National Vision 2030, and Kuwait’s New Kuwait 2035. These roadmaps are driven by a common goal of developing non-oil sectors to achieve sustainability and maintain the GCC’s relevance in a post-oil future.
The Importance of Regulatory Compliance for GCC Businesses
GCC businesses must adapt proactively to the region’s regulatory changes to maximise growth opportunities. This is where leaders, such as the board of directors, become crucial in maintaining robust business compliance systems for stronger governance and risk management.
Establishing strong business compliance systems promotes the following benefits:
- Enhanced Reputation: Compliance demonstrates an organisation’s strong commitment to lawful and ethical practices mandated by authorities. It improves public perception over the long term and provides a strategic advantage for strengthening relationships with stakeholders and boosting trust with customers and authorities.
- Financial Sustainability: One way to boost regulatory compliance is by investing in digital tools with the right capabilities, such as workflow automation, real-time reporting, and data encryption. These tools enable compliance teams to streamline and scale their processes efficiently, avoiding costly penalties caused by non-compliance. Integrating digital tools like a council portal has become easier with the emergence of Regulatory Technology (RegTech) in the GCC. Adaptable to industry-specific regulatory needs, council portals are designed to optimise operational efficiency by centralising compliance-related activities, which reduce manual errors and administrative burdens.
- Stronger Data Privacy: Experts forecast that economic diversification efforts will boost the digitalisation transformation market in the GCC by 24.8% from 2024 to 2032. To keep up with the surge, GCC nations are innovating their data privacy laws to match international standards like GDPR and CCPA. Businesses can leverage this by building trustworthy data privacy systems to position themselves as market leaders in this digital age.
- Improved Market Access: Organisations must prioritise compliance to enhance their competitiveness in the global market and attract new investors. According to Ernst & Young, Foreign Direct Investments (FDIs) in the GCC increased by 512% in business services and 373% in software and IT between 2018 and 2023. This reflects the growing confidence of foreign markets in the region as it advances its national development plans.
- Operational Alignment: Regulations standardise key business processes by setting consistent guidelines and requirements, promoting consistency and accountability. This urges organisations to adopt best practices, reducing risks and increasing efficiency.
Examples of Regulatory Violations in the UAE
The UAE enforces stringent measures to ensure compliance and protect consumer rights. Gain insights as to how authorities uphold UAE regulations through real-life cases below.
R.J. O’Brien (MENA) Capital Limited
The Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA) is mainly responsible for overseeing financial activities and enforcing anti-money laundering measures within the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC). In 2023, DFSA revealed that the company of R.J. O’Brien Capital Limited didn’t have proper compliance controls and systems when it acquired a new brokerage in the same year. Specifically, it failed to maintain electronic records of transactions, comply with Intercontinental Exchange (ICE) Europe and ICE USA rules on block trading and reporting, and meet DFSA’s client inboard rules.
Incurring financial and reputational damage, RJO MENA initially received a fine of 10,251,789 AED that was lowered to 5,023,375 AED after signing an Enforceable Undertaking, in which they agreed to implement immediate corrective actions.
Designated Non-Financial Business and Professions (DNFBP) Entities
Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBPs) are non-financial entities (e.g., real estate agents, lawyers, accountants, gambling establishments, and precious metals and stones dealers) susceptible to money laundering and terrorist financing activities.
To regulate DNFBPs and their inherent risks, Anti-Money Laundering and Countering Financing of Terrorism (AML/CFT) regulations mandate the implementation of comprehensive risk management measures. To manage risks, businesses must develop internal controls, conduct customer due diligence, maintain detailed records, and report suspicious transactions to the relevant authorities.
In 2023, the Ministry of Economy fined 29 DNFBP companies 22.6 million AED for non-compliance with Federal Decree-Law No. 20 of 2018 of the AML/CFT regulation. This decisive action by the Ministry of Economy demonstrates its dedication to establishing a risk-free business environment in the UAE.
Sector-Specific Regulations Shaping UAE Industries
The UAE needs support for sector-specific regulations as it continues to expand to non-oil sectors. Operating within a consistent framework provides a clear path, allowing sectors to achieve sustainable growth and maintain global competitiveness.
Here are examples of key regulations shaping industries across the UAE.
Healthcare
The Health Data Law (Federal Law No. 2 of 2019) governs health data management across providers, whether direct or indirect services. It sets specific standards for data processing, security, localisation, and retention. The Ministry of Health and Prevention is the main regulator responsible for establishing a centralised data exchange system where organisations can securely collect and transfer health data among authorised users. Non-compliance with this law constitutes disciplinary action and monetary fines ranging from 1000 AED to 1 million AED.
Banks and Credit Unions
The Central Bank of the UAE (CBUAE) regulates banks and other financial institutions across jurisdictions. Under the Federal Decree-Law No. 14 of 2018, they have the authority to:
- Formulate and implement monetary policies that align with national economic goals and strategy.
- License financial activities across banks and other financial institutions to standardise practices and promote adherence to international standards.
Uphold stringent risk management measures to ensure licensed financial institutions protect consumer data. - Oversee the adoption of FinTech innovations such as electronic payment systems and digital currencies.
- Monitor the insurance industry to maintain fair practices and protect the rights of policyholders.
Nonprofits
Charitable and nonprofit organisations in the UAE are bound by Federal Law No. 2 of 2008 on Public Welfare Associations and Non-Governmental Organisations. It guides organisations on licensing requirements, operational transparency, and compliance to ensure alignment with national public welfare objectives.
To ensure adherence to this law, the Ministry of Community Development processes the licensing of nonprofit organisations in coordination with local authorities to ensure the legitimacy of their operations. To secure the license, nonprofits are required to submit the following:
- Annual reports consist of financial statements and project breakdowns.
- Periodic financial audits across departments to foster transparency and accountability.
- Renewal of registration
Universities
The UAE is committed to enhancing its education system with the National Strategy for Higher Education 2030. Under the supervision of the Ministry of Education, the strategy started the Inspection Framework to ensure the delivery of high-quality education. It requires institutions to implement standards based on relevant UAE laws, international best practices, and world ranking indicators.
The Inspection Framework is divided into three sections:
- Inspection Approaches: Details the required components of the inspections, such as methodology, operational management types, and frequency of compliance inspections.
- Inspection Process: Outlines the step-by-step inspection process, its coverage, and corrective action plans.
- Standards for Compliance Inspection of Higher Education Institutions: Enumerates the compliance inspection standards, which include 13 standards and 20 compliance indicators.
Innovative Trends in Regulatory Compliance GCC
Stay informed on the latest regulatory developments driving FinTech, RegTech, and data privacy across the GCC.
Improving the FinTech landscape
GCC is proactively advancing new regulations to support the growth of FinTech in the region. In 2023, CBUAE introduced the Finance Companies Regulation to promote responsible financial activities amidst the rising demand for buy now, pay later (BNPL) as a short-term credit scheme. Following this trend, the Saudi Arabia Central Bank (SAMA) issued its own BNPL guidelines in December 2023 to regulate licensing, minimum capital thresholds, and consumer protection.
Bahrain, a pioneer of open banking in the region, has required licensed financial and banking institutions to comply with its new Open Banking Framework (OBF). In line with the primary rules issued in 2018, the OBF provides in-depth guidelines for its application to institutions, such as operational guidelines, security standards, customer experience guidelines, technical open Application Programming Interface (API) specifications, and data governance.
Enhancing consumer protection and anti-money laundering
The GCC strives to create a fair, transparent, and secure business environment for individuals and businesses. For example, Saudi Arabia implemented its Data Protection Law in 2021, and the UAE introduced its own in 2022. This emphasises the growing complexity of data privacy management as Gulf nations welcome digitalisation. In finance, the CBUAE, SAMA, and Qatar Financial Centre Regulatory Authority are strengthening regulatory compliance by aligning money laundering regulations with international standards.
Rise of RegTech
The GCC is witnessing the rise of RegTech to assist governments and businesses in facilitating secure and ethical digitalisation in sectors such as logistics and finance. In 2024, the RegTech market in the Middle East grew to 1.66 million USD, with a forecasted CAGR of 18.5% until 2029. This highlights the increasing importance of RegTech in the region’s digital transformation. With RegTech in business compliance, teams can use predictive analytics, blockchain, and automation to enhance operational efficiency, optimise compliance-related costs, and strengthen risk management.
Streamline Regulatory Compliance in the GCC with Convene Board Portal
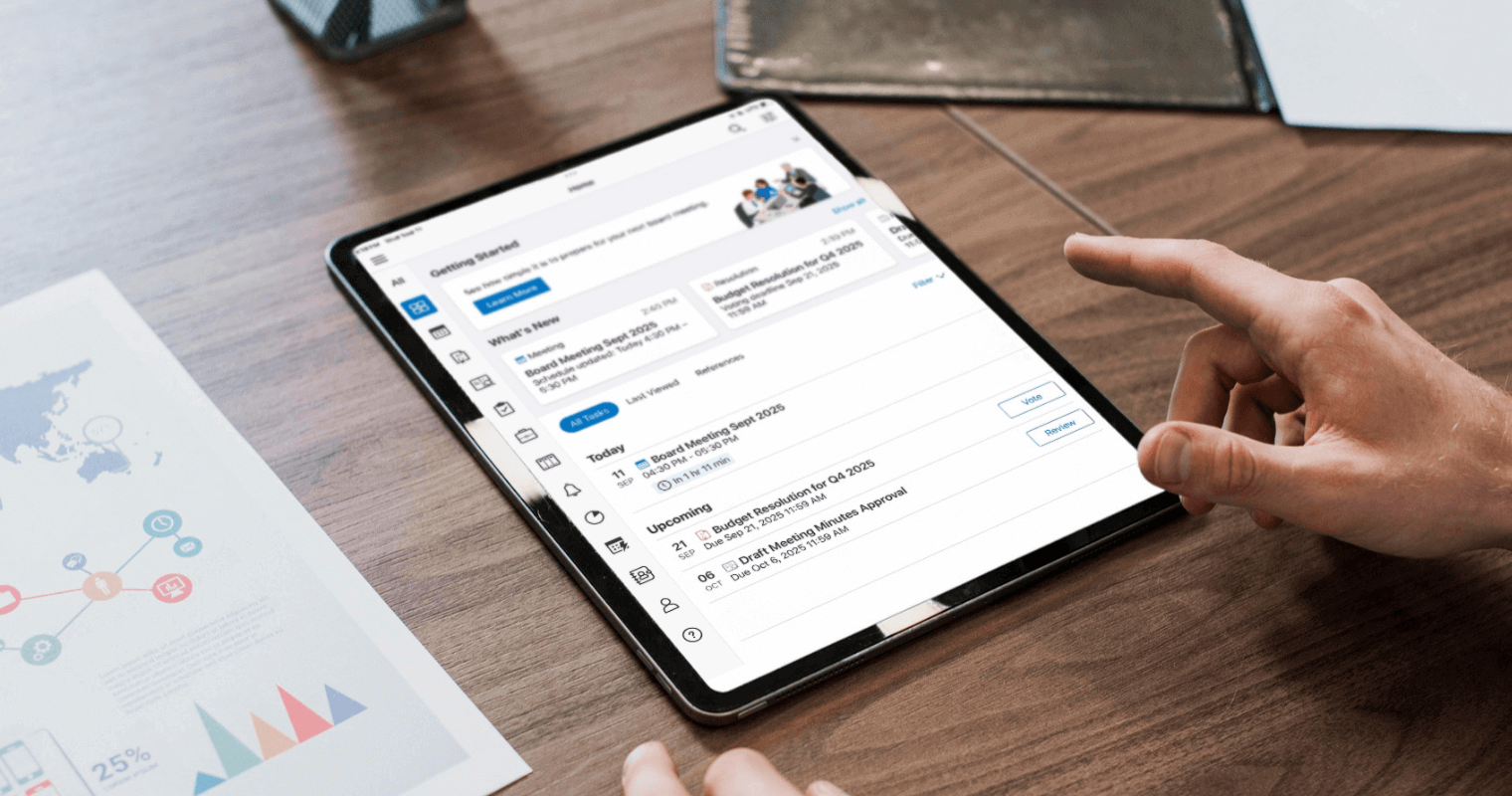
Compliance in the UAE and the broader GCC has become more complex as governments implement new regulations and industry standards. As the main governing body, the board of directors must lead in applying these changes in their organisations to avoid penalties and maintain a strong track record.
Leveraging technology has become an effective approach to streamlining compliance processes, including risk analysis discussion, financial reporting, tax e-filing, and document signing. Board portals or council portals are digital tools packed with advanced features board members can rely on to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of compliance management.
Convene is a leading board portal in the UAE and GCC, trusted by banks, healthcare institutions, and government agencies. Designed with a comprehensive suite of features, the Convene board portal empowers leaders to meet regulatory requirements seamlessly, no matter where they operate.
With Convene, businesses in the UAE can experience:
- Real-time Document Collaboration: Facilitate direct, secure document editing on compliance materials for accurate and up-to-date records.
- Secure Approvals with Digital Signature: Leverage Convene’s digital signature solutions for approvals across decision-makers. Gain access to reliable third-party providers such as DocuSign, E-Güven, Infile, and Sayen by stc to ensure approvals meet GCC’s legal requirements.
- Efficient Meeting Management: Arrange, schedule, and run board meetings within one location. Convene’s intuitive interface allows board members to receive meeting invitations, review agendas, and track action items effortlessly.
- Audit Trails: Capture and log every activity within the portal, including document access, edits, and comments to promote accountability among board members.
- Encrypted Document Sharing: Boost the confidence of board members when sharing documents with Convene’s encrypted board portal. Receive and submit documents without risks of data breaches and leaks.
- Customisable Alerts and Notifications: Tailor alerts, meeting invitations, and other notifications to inform stakeholders about regulatory deadlines, compliance updates, and action items.
- Cross-Platform Access: Access compliance documents and other board materials from any device, eliminating delays due to inaccessibility issues.
Execute next-level board governance with Convene! Book an app walkthrough to experience firsthand how the Convene board portal streamlines your compliance management.
Jean is a Content Marketing Specialist at Convene, with over four years of experience driving brand authority and influence growth through effective B2B content strategies. Eager to deliver impactful results, Jean is a data-driven marketer who combines creativity with analytics. In her downtime, Jean relaxes by watching documentaries and mystery thrillers.











