The reality is that the world is constantly changing, and it’s not all for the better. Climate change, dwindling natural resources, and widening social inequalities are pressing issues that affect every corner of the planet. Our ecosystems have long been threatened, pollution levels are alarming, and many communities lack access to basic needs like clean water and education. These global challenges emphasise the need to rethink our ways — how we live, work, consume, and interact with the world.
This is where sustainability offers a path forward.
What is sustainability?
Sustainability is about creating a balance between the economy, society, and the environment to ensure resources are used responsibly and preserved for the future. In business, it means operating in ways that minimise, if not completely avoid, harm to people and the planet while driving growth. This sustains operations and progress while responsibly safeguarding resources and the environment for years ahead. By prioritising sustainability, companies not only protect limited resources but also level up their reputation, attract top talent, and secure their long-term success.
How important is sustainability?
Sustainability is a significant concern as it balances environmental protection, social equity, and economic growth by encouraging responsible use of resources and accountability of stakeholders. This addresses critical challenges while securing resources and opportunities for future generations. Sustainability is essential in:
- Protecting the environment: Sustainable practices address climate change, reduce pollution, and preserve our biodiversity by pushing for renewable energy and cutting our dependence on finite resources, especially those that produce greenhouse gas emissions. These efforts safeguard our essential ecosystems, and keep our air and water clean, while encouraging cooperation to tackle environmental issues through community engagement and awareness.
- Advancing social responsibility: This reduces inequality by improving access to healthcare, education, and housing while promoting diversity, equity, and inclusion. Companies that adopt these ethical practices strengthen their relationships with stakeholders, align business decisions with broader societal needs, and build a reputation for accountability and integrity.
- Ensuring economic sustainability: A sustainable economy prioritises growth that avoids harming the environment or society, emphasising solutions that are greatly innovative. Policies encouraging green technologies and sustainable investments contribute to adaptable and financially stable systems supporting opportunities and overall development.
- Preparing for the future: Businesses integrating sustainability into their strategies are better prepared for evolving demands. By innovating to meet modern expectations and highlighting their contributions at present and for the future, companies increase their relevance, trustworthiness, and ability to thrive in a competitive landscape.
What are the 6 Rs of sustainability?

Sustainability is not simply about preserving the environment but can be viewed as an approach that can transform how producers and consumers interact with the planet. Originally, there were only the 3 Rs — Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle — as part of a growing environmental movement in the 1960s and 70s. Over time, many industries have adopted these principles to cut down on waste, save energy, and encourage sustainable practices.
It then evolved into the 6 Rs of sustainability — Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Rethink, and Repair — that offer more actionable steps to minimising environmental harm while maximising our resources. Adopting these 6 principles of sustainability can provide companies and communities with meaningful changes that protect our planet, create economic opportunities, and improve quality of life.
Let’s explore the 6 Rs of sustainability, their impact on consumer behaviour, and how they contribute to a sustainable future.
Reduce
Reducing waste and energy consumption is the foundation of sustainability. By cutting down on unnecessary materials and processes, businesses can lower their environmental footprint and save costs. For example, going paperless and optimising energy use can yield significant long-term benefits while conserving resources for future generations, which is being done by the Bank of America’s digital-first products and services.
Consumers are learning to minimise waste by buying only what they need. For instance, people now prefer products with minimal packaging or brands that support eco-friendly practices. This shift discourages overconsumption and encourages a culture of simplicity.
Reuse
Reusing materials prevents waste from being discarded prematurely and extends their lifecycle. The idea of reusing has inspired consumers to repurpose items instead of discarding them. From using reusable bags and containers, people are finding creative ways to extend product lifespans. The green soju bottle is an example, where major producers in South Korea voluntarily agreed to standardise soju bottles and support bottle deposit systems to collect them for reuse.
Recycle
Recycling involves transforming waste into new, usable products. Implementing effective recycling or upcycling programs, such as separating materials at the source, can significantly reduce landfill contributions. Recycling also provides an opportunity to recover valuable materials and reintegrate them into production cycles, promoting a circular economy.
Awareness campaigns about proper disposal methods have empowered individuals to contribute to circular economies, where waste is transformed into new resources.
Repair
Repairing items instead of discarding them promotes the efficiency of resources and reduces waste. Encouraging a culture of maintenance and restoration can extend the life of products and reduce the demand for new resources. Repair programs, whether for electronics or clothing, are excellent examples of this principle in action. This includes Microsoft working with iFixit to offer tool kits designed for its self-repair initiative of their devices.
The repair mindset motivates consumers to fix items rather than replace them straight away. Whether it is mending clothes, repairing electronics, or restoring furniture, this trend reduces waste and promotes resource conservation.
Refuse
Refusing unnecessary or harmful materials, such as single-use plastics, helps reduce environmental damage at the source. Businesses can choose more sustainable alternatives and encourage customers to adopt similar habits. This proactive approach tackles waste before it becomes an issue.
Refusing unnecessary or single-use items has gained traction. Many consumers and a growing number of businesses now reject plastic straws, disposable cutlery, or excessive packaging. This mindful refusal not only reduces landfill waste but also pushes companies to adopt sustainable alternatives.
A global movement called Plastic Free July calls for the behaviour change of refusing single-use plastic consumption, resulting in its effective reduction. Participants in 2021 were able to reduce 1.2 billion kg of waste sent to landfills, 900 million kg of recyclable materials, and 0.3 million tons of plastic, a movement that started with just 40 people and now involves millions around the world. This was supported by different institutions, governments, and companies and influenced the global plastic treaty at the UN’s environment assembly.
Rethink
The last R — Rethinking — challenges businesses and individuals to adopt innovative approaches to sustainability. This means reassessing processes, products, and goals to align with environmental priorities.
For instance, supply chains can be upgraded or transformed to prioritise eco-friendly practices and integrate sustainable materials and processes into their operations. One such case is Tesla’s sustainable global energy economy plan through a renewable-powered grid, electrified transportation, and minimising the extraction of resources.
Rethinking consumption encourages consumers to question their buying habits. People increasingly consider a product’s lifecycle, ethical sourcing, and environmental impact, driving demand for sustainable and responsibly made goods and services.
How do you apply the 6 Rs for your company?
The 6 Rs of sustainability — Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Rethink, and Repair — serve as a comprehensive guide for companies seeking to create meaningful changes in operations that resonate beyond corporate social responsibility. Here’s how your company can strategically apply these principles:
- Assess opportunities and plan strategically: Start with a detailed evaluation of your operations to identify areas where sustainability practices can be introduced or improved. Use this assessment to design a clear and actionable plan that prioritises high-impact areas while making sure the company’s mission and goals are aligned. A well-thought-out ESG strategy guarantees efforts are meaningful, measurable, and scalable.
- Reduce waste and optimise resources: Implement resource-saving measures, such as transitioning to paperless systems or minimising packaging materials. Reducing waste not only lessens the environmental footprint but also improves operational efficiency and cost management.
- Reuse and repurpose creatively: Find innovative ways to extend the life cycle of materials by reusing or repurposing them. This could involve rethinking production waste or utilising refurbished equipment, demonstrating a commitment to sustainability and resourcefulness. Such is the case with Samsung’s upcycling program, which repurposes old smartphones into smart home devices, contributing to a circular economy by reducing e-waste, extending product life cycles, and encouraging reuse of resources.,
- Recycle responsibly and build systems: Establish and promote robust recycling programs across the organisation. Proper waste segregation and adherence to recycling standards help ensure compliance while visibly reinforcing the company’s environmental responsibility. For example, Coca-Cola established a “World Without Waste” initiative that aims for packaging that is 100% recyclable and uses 50% recycled material.
- Rethink processes and innovate for sustainability: Reevaluate traditional processes to identify eco-friendly alternatives and opportunities for innovation. An example is how Walmart committed to rethinking its global operations and transitioning to renewable energy sources like wind and solar installations. Encouraging teams to develop new products or workflows that align sustainability goals with business objectives, also encourages creativity and long-term value for the company.
- Engage stakeholders and advocate for action: Cultivate a culture of sustainability by actively involving employees, clients, and partners in the mission of climate change and social responsibility. Communicate goals transparently through sustainability reporting and provide opportunities for everyone to contribute to the cause. Strong stakeholder engagement reinforces the company’s leadership in sustainability and fosters collective ownership of company goals.
What are the three pillars of sustainability?
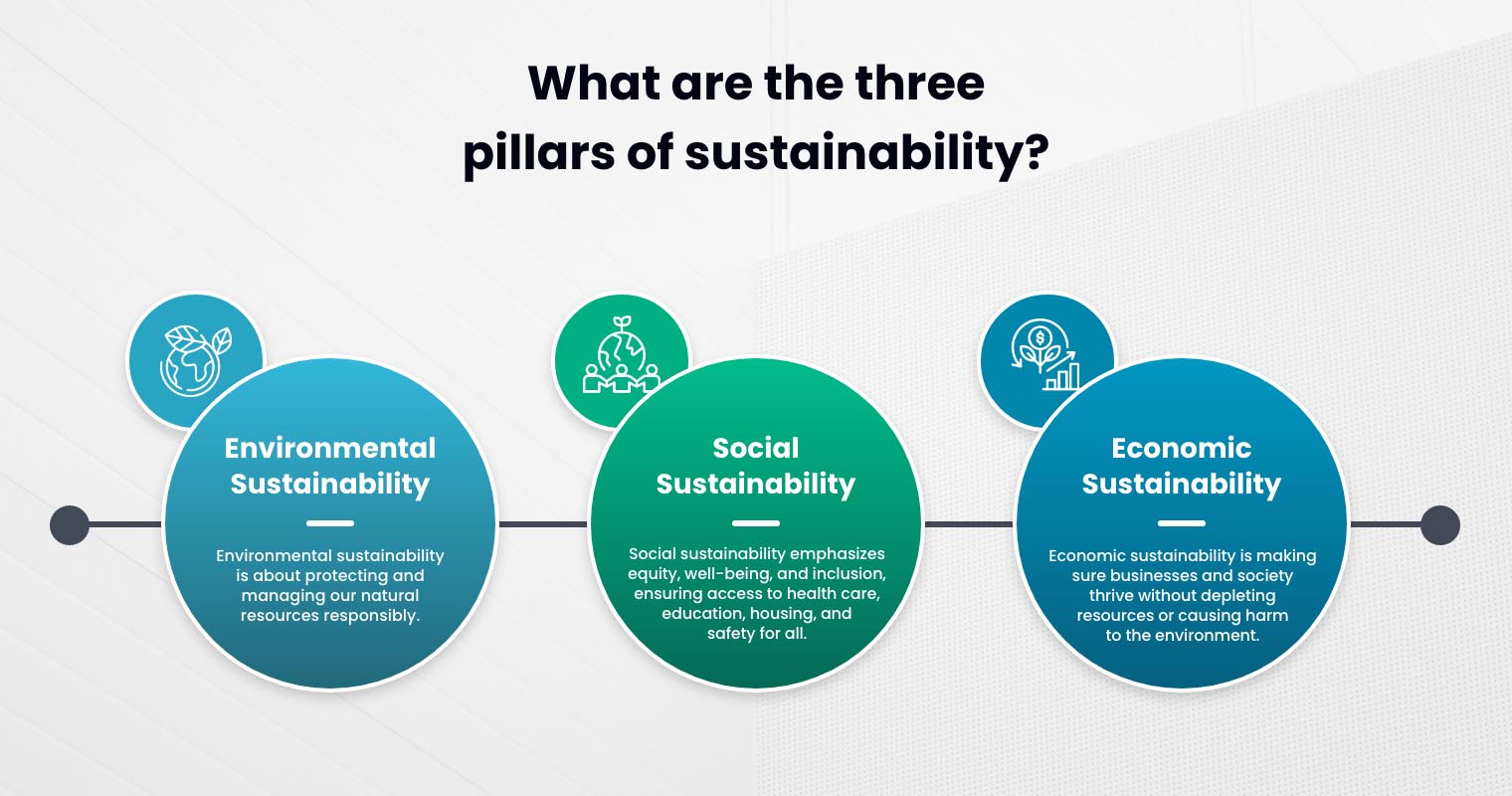
Sustainability revolves around three interconnected pillars: environmental, social, and economic sustainability. Together, these dimensions create a framework for balancing the needs of the present with those of future generations. These pillars provide actionable guidelines for addressing pressing global issues, such as climate change, inequality, and resource depletion. Below is an overview of each pillar and its importance.
Environmental Sustainability
Environmental sustainability is about protecting and managing our natural resources responsibly. It includes practices, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving biodiversity, minimising pollution, and conserving energy and water resources.
This pillar ensures the health of ecosystems, which directly affects human well-being and the survival of countless species. For example, adopting sustainable agricultural practices and a circular economy helps preserve resources for future generations.
Social Sustainability
Social sustainability focuses on equity, well-being, and inclusion, addressing needs such as health care, education, housing, and safety for all members of society. It fosters connected and resilient communities by reducing inequalities and supporting diversity. For instance, fair access to resources and opportunities promotes social harmony and justice. By affirming a good quality of life, this pillar reduces societal vulnerabilities, improves social cohesion, and creates a foundation for sustainable economic and environmental strategies.
Economic Sustainability
Economic sustainability is making sure businesses and society thrive without depleting resources or causing harm to the environment. It prioritises responsible resource management, innovation, and financial stability to create long-term prosperity. Practices such as aligning investments with sustainability goals and adopting circular economic models reduce waste and maximise resources. This benefits economies while safeguarding the planet.
What role does ESG play in sustainability?
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria are essential tools for integrating sustainability into business and investment decisions. They align closely with the pillars of sustainability by providing measurable standards for assessing and improving a company’s sustainable practices.
- Environmental (E): This examines how organisations manage their impact on the environment, such as reducing emissions, conserving energy, and adopting eco-friendly technology.
- Social (S): This aligns companies with their social sustainability goals. It evaluates workplace diversity, labour practices, and contributions to societal well-being.
- Governance (G): Governance focuses on transparency, accountability, and ethical business practices. Strong ESG governance supports environmental and social efforts by building trust with stakeholders.
Why ESG Matters
ESG bridges the gap between sustainable development goals and real-world action. By integrating ESG factors into decision-making, businesses can align their operations with sustainability goals, build trust with investors, and contribute to global challenges like climate change and social inequality. Companies adopting ESG principles often observe enhanced financial performance and risk management. For example, reducing energy consumption not only benefits the environment but also cuts costs, providing a dual advantage.
ESG provides a structured framework to measure and manage these efforts, helping companies align their operations with global standards and stakeholder expectations. ESG reporting takes this a step further by offering a transparent account of an organisation’s performance, allowing stakeholders to assess its impact and commitment to sustainable development. By fostering accountability and showcasing progress, ESG reporting ensures businesses not only meet compliance requirements but also contribute meaningfully to a more sustainable future.
Drive Sustainability Forward with Convene ESG
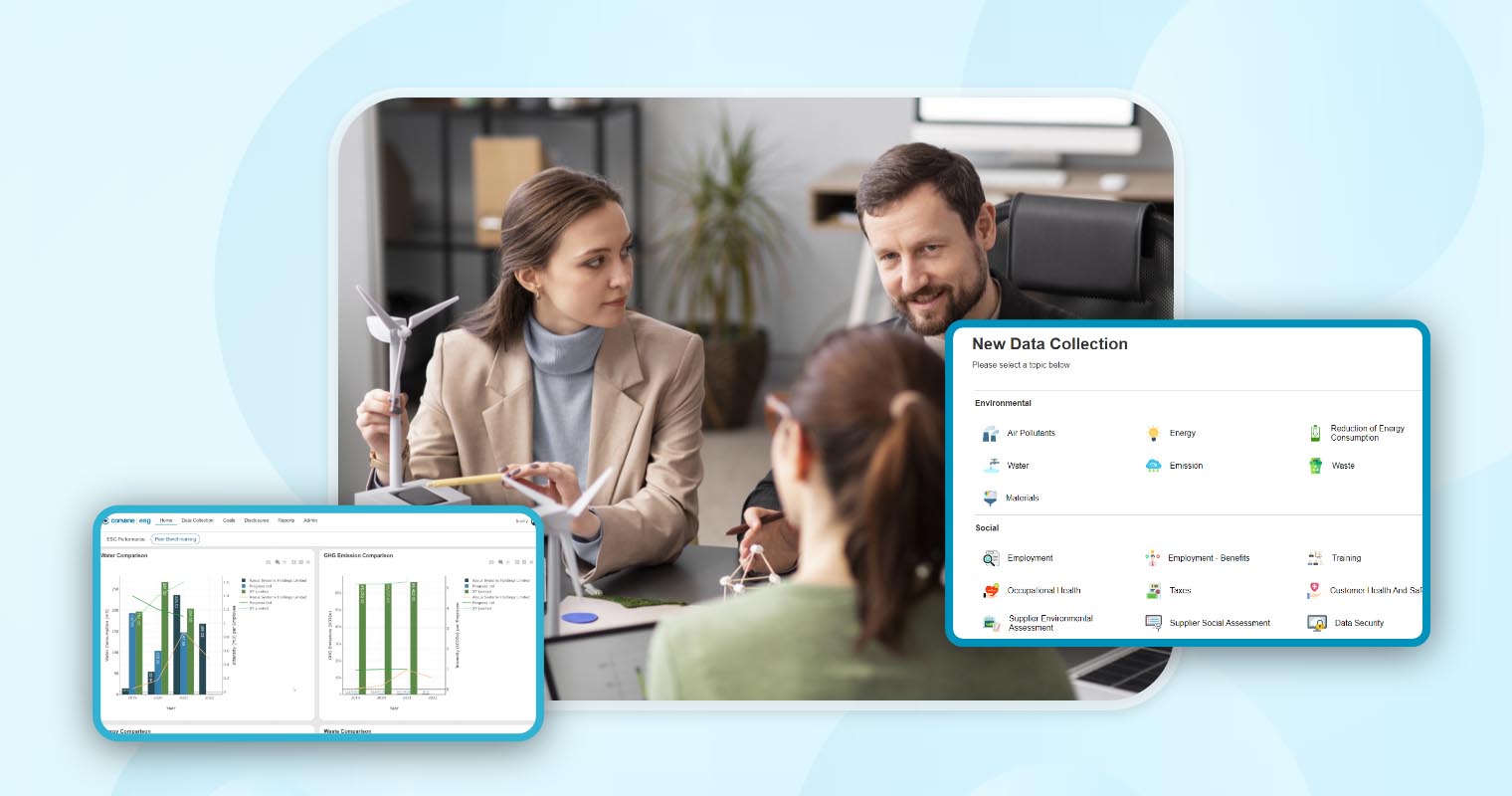
Achieving balance across environmental, social, and economic factors requires thoughtful strategies and transparent reporting. Sustainability reporting pushes for organisations to not only implement sustainable practices but also share their impact on stakeholders and the environment. Whether it’s reducing emissions or improving social responsibility, organisations require a solution to manage the complex tasks of data collection, analysis, and compliance. The key lies in streamlining this process with sustainability software to make it efficient and impactful.
Convene ESG steps in as the ESG reporting software that is designed to measure, manage, and elevate sustainability efforts. This ESG software centralises data collection, ESG reporting, and collaboration. With features like pre-built templates aligned with global sustainability frameworks and local standards, dashboards for tracking progress, and seamless team integration, Convene ESG makes sustainability reporting manageable and effective.
Take the first step to simplify your sustainability efforts. Schedule a demo today!
Pat is a Content Writer, focusing on informative and purposeful content for Convene ESG. She has written for sustainable living and art exhibitions, and took part in research and communication projects linked to the UN's Sustainable Development Goals, further diving her into sustainability and ESG values. Outside of marketing and content, she explores new subjects in film, drawing, and occasional overthinking.














