Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors have been critical to a company’s long-term sustainability in recent years. However, while environmental and social issues continue to gain massive attention from the media and businesses alike, the last criterion — governance — often remains overlooked. A recent Morningstar Sustainalytics survey on sustainability professionals showed that out of over 500 respondents, 46% put corporate governance at the bottom of their ESG efforts, demonstrating a significant gap in their perception and prioritisation.
This article highlights the importance of governance in ESG, tackling its key factors and best practices to enhance your business’s corporate governance.
What is ESG Governance?
ESG Governance refers to the framework that guides a company’s decision-making regarding its ESG programs and practices. These are the policies, procedures, and structures that ensure it operates ethically, sustainably, and in the best interest of the stakeholders. Think of it as the foundation that balances and connects the organisation’s environmental and social efforts.
Yet despite its importance in sustainable business practices, many corporations aren’t prioritising corporate governance, according to the Morningstar Sustainalytics survey. This suggests that organisations may be undervaluing governance, which can weaken their overall ESG efforts. This gap can hinder their sustainability progress and goals since strong governance is crucial for accountability, transparency, and ethical management.
Understanding the Importance of ‘G’ in ESG
So, what does governance mean in ESG? Companies with strong ESG governance practices are better equipped to adapt to changing market conditions and societal expectations. They are more likely to maintain long-term success by aligning their operations with sustainable practices and ethical standards. Studies show that organisations prioritising and implementing best governance practices tend to perform better financially. They achieve organisational objectives more consistently and attract a broader investor base than those with weaker governance frameworks.
Conversely, poor corporate governance can severely impact a company’s integrity, reliability, and ability to raise capital. It may also hinder its efforts to meet ESG goals effectively.
Additionally, strong governance frameworks encourage a culture of responsibility and ethical behaviour within the organisation, which can improve employee morale and retention.
ESG Governance Factors and KPIs
Effective ESG governance uses clear metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to assess a company’s environmental impact management, social responsibilities, and governance practices. This table outlines areas and indicators that companies must focus on to improve transparency, accountability, and sustainability:
| Factors | Key Indicators |
|---|---|
| Knowledge, experience, power allocation, decision-making processes, independence, and empowerment of compliance function | |
| Competencies, diversity, structure, committees, oversight capacity, independence | |
| Compensation, promotion, reporting structures, prohibited conduct, disciplinary measures | |
| Company purpose, values, culture, integrity beyond compliance, ESG integration, pursuit of and reporting on KPIs | |
| Tax compliance, anti-tax avoidance, tax disclosures Must also factor in ownership, subsidiaries/holdings, open contracting, lobbying, charitable donations, countries of operation | |
| Compliance with ESG and other industry-specific regulations, number of regulatory violations or fines and remediation, transparency in regulatory disclosures | |
| Risk mitigation strategies, past performance, regulatory compliance, segregation of duties, audit independence, shareholder rights, information governance, cybersecurity measures | |
| Report transparency, data accuracy and completeness, timeliness |
Improving ESG governance means working on one or several of these ESG governance issues.
What does a good ESG governance structure look like?
An ESG governance structure is a framework within an organisation that ensures all ESG considerations are integrated into corporate strategy and operations. This structure varies from one company to another, but typically includes dedicated roles and responsibilities for overseeing and managing ESG-related matters. Here’s a basic structure chart:
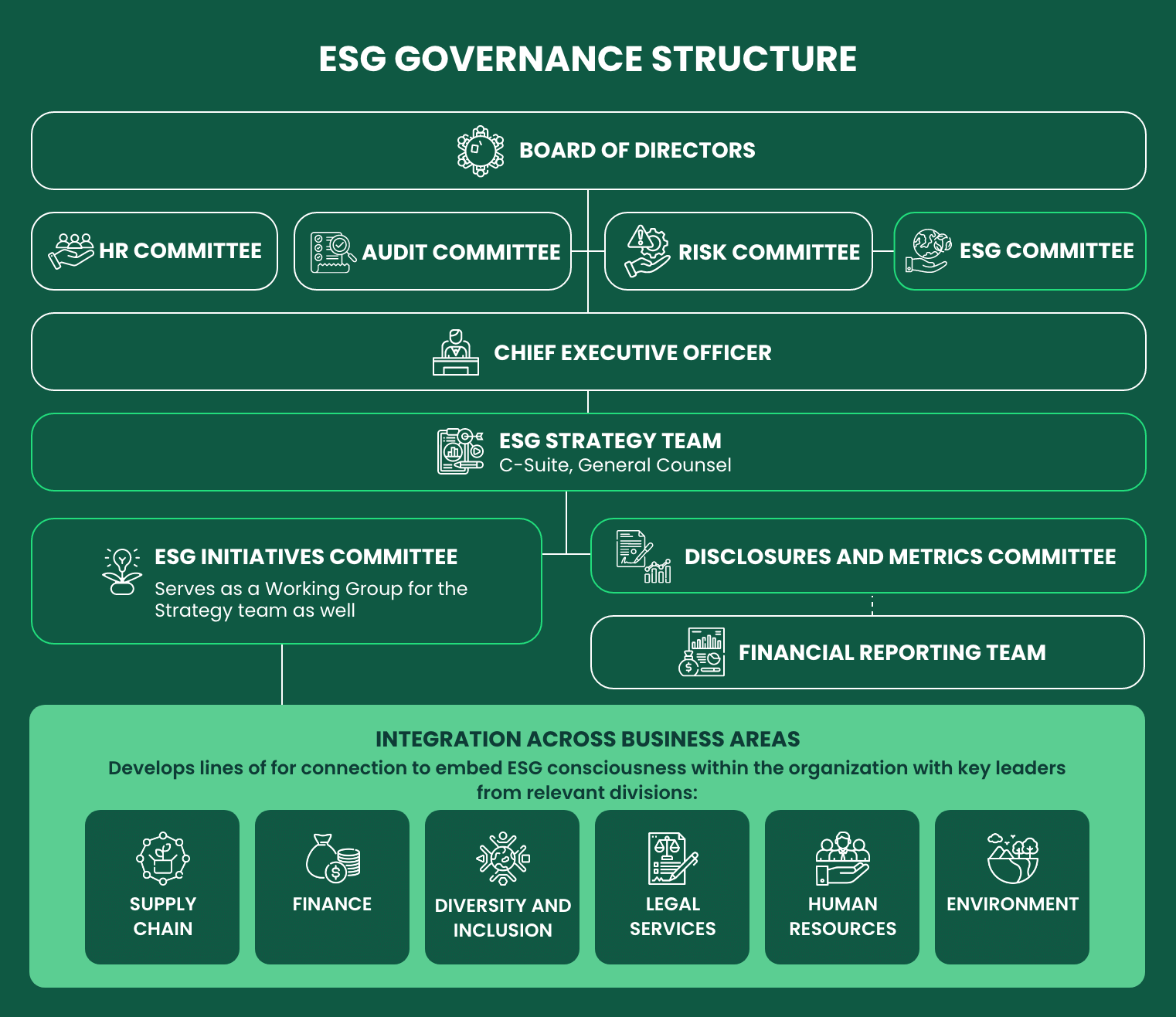
Original concept from CrossCountry Consulting
There is no one-size-fits-all model, but it is important that companies are clear with the roles of each key individual and are able to adapt flexibly to the ESG governance needs of the business.
Benefits of Good ESG Governance Structure
When supported by a strong governance structure, your environmental and social efforts will become more effective and impactful. It will also help:
Create long-term value
A company with a strong ESG corporate governance structure often achieves better financial performance over the long term. By integrating sustainability into their core strategies, these organisations mitigate risks related to regulatory compliance, environmental impacts, and stakeholder relations. At the same time, they capitalise on opportunities for innovation and efficiency improvements, which can lead to cost savings and revenue growth.
Moreover, because positive ESG performance enhances reputation and brand value, it attracts customers who prioritise ethical and sustainable products and services. A report by RepTrak shows that a high ESG score can result in a 67% willingness to buy, compared to 10% of those with a low score.
Attract the right investors
Investors now care more about the sustainability of the companies they invest in. This approach, more commonly known as sustainable investing, often directs investment capital to companies that seek to combat environmental issues such as climate change while balancing corporate responsibility.
If your organisation has a clear and robust ESG strategy, it demonstrates its commitment to responsible business practices. This can attract socially conscious investors and institutional funds that share the same core values. By appealing to these investors, companies can access capital faster and at lower costs, enhancing financial stability and growth prospects.
Promote sustainable practices
Establishing strong corporate governance ultimately encourages companies from the top down to adopt and maintain sustainable practices throughout their operations. This could include small steps like recycling and waste segregation, encompassing larger initiatives like reducing carbon footprints, conserving natural resources, and ensuring ethical labour practices. By integrating sustainability into the corporate culture, companies not only comply with industry-related regulatory requirements but also contribute to the well-being of the environment and society.
ESG Best Practices in Governance
Good governance is the backbone of a successful business. If you plan to take the first step into better ESG governance (or you’ve already begun), let these tips guide your journey. Here are the best practices to follow to ensure business growth and success:
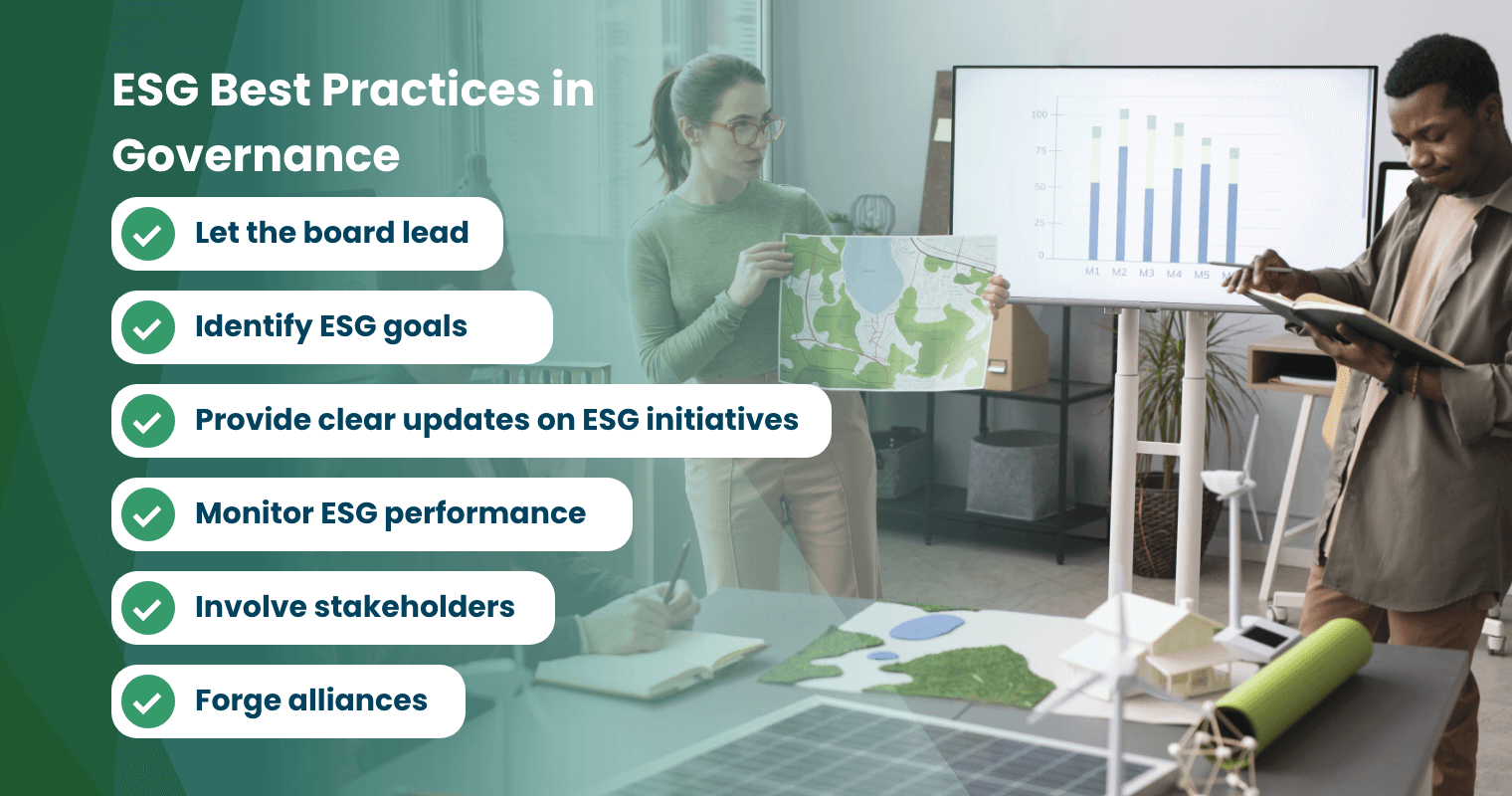
Let the board lead
Your board of directors should lead an effective ESG governance structure. They set the tone at the top and ensure that ESG principles are embedded throughout the organisation. From the board comes a dedicated ESG committee and sustainability officers to oversee strategies and initiatives. This committee should include members with expertise in sustainability and corporate governance.
Identify ESG goals
Clearly identify your ESG goals and set measurable objectives that align with your company’s values and long-term strategy. These objectives must be specific and attainable within your established time frame. KPIs can help track your progress.
Provide clear updates on ESG initiatives
Transparency is key to building trust and credibility in ESG efforts. Companies should regularly disclose their ESG performance, initiatives, and challenges to stakeholders through business websites, investor meetings, and sustainability reports. Transparent ESG reporting demonstrates your commitment, allows for accountability, and encourages continuous improvement.
Monitor ESG performance
Continuous monitoring and improvement of ESG performance metrics are crucial. Once initiatives are underway, you must keep an eye on their impact and effectiveness. This involves collecting relevant data, analysing trends, and benchmarking against industry standards. Regular assessments enable companies to identify areas for improvement and demonstrate progress over time.
Involve stakeholders
Engaging stakeholders—such as investors, employees, customers, and community members—is essential for effective governance in ESG. By understanding their perspectives and expectations, you can prioritise issues that matter most to them and adjust your strategies accordingly.
Forge alliances
It takes a village to achieve collective sustainability goals. By partnering with industry peers, non-governmental groups, and other stakeholders, you’ll have more hands on deck to support your efforts, exchange best practices, and drive action toward common goals.
The Future of ESG Corporate Governance
The future will demand that companies embed ESG considerations deeply into their corporate strategies. This means integrating sustainability goals into core business operations, ensuring accountability from the boardroom to the front lines. One noteworthy trend to focus on is the transition to a plastic circular economy.
The global treaty to end plastic pollution is expected to be finalised by the end of 2024, which could catalyse a transformative shift towards sustainable practices across industries worldwide. This treaty can potentially set new standards for producing, using, and disposing of plastics, prompting companies to innovate toward circular economy models. Once approved, the treaty could drive significant investments in a circular economy for plastics, potentially meeting the required $65 billion annually through 2040.
However, achieving scalability and widespread adoption of circular practices will require concerted efforts across sectors and regions. Several regulations, such as the EU’s Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation and the Extended Producer Responsibility law in the Philippines, have already been introduced to address this issue in recent years.
Companies can start proactively integrating circular economy principles into their operations to respond to these market expectations. This includes redesigning products for recyclability, adopting sustainable packaging solutions, and investing in advanced recycling technologies, among other initiatives. High-level solutions, including collaborating with stakeholders and leveraging innovation in waste management, will also be essential for successfully preparing and capitalising on the transition to a plastic circular economy.
Drive Better ESG Governance with Convene ESG
ESG governance is no longer a peripheral concern but a central component of corporate strategy. This means there would be much more emphasis on ESG integration, from decision-making processes to day-to-day activities. Companies will need to adopt advanced tools and platforms to manage and report on their ESG performance effectively. Fortunately, technological solutions like ESG software have emerged to lighten the burden of ESG reporting.
Convene ESG, a comprehensive ESG reporting software, offers tools and services that help companies assess, manage, and improve their ESG performance from end to end. This centralised ESG software helps streamline processes from report preparation to generation with pre-built and customisable templates that follow global ESG disclosure standards like GRI, CSRD, TCFD, and ISSB.
Organisations can also get support from our team of experts and partners through consultations, assurance, and integrations.
Book a demo today to find out how you can reinforce your corporate governance with Convene ESG.















