Businesses that want to stay ahead in today’s competitive market must step up their carbon reporting. More than ever, governments, investors, and partners are asking for clear disclosures on environmental impact. And after the 29th National Climate Change Conference (COP29) in late 2024, it’s clear that meeting basic regulations isn’t enough. To secure sustainable financing and build trust with top industry players, companies must align with global standards and go beyond what is legally required.
One effective way to do this is through accurate greenhouse gas (GHG) reporting. Various standards have emerged to help organisations navigate their overall emissions. One of which is the ISO 14064 Standard. Explore in this article how ISO 14064 benefits companies in managing, reporting, and verifying GHG emissions.
What is ISO 14064?
ISO 14064 is a globally recognised three-part standard that specifically addresses greenhouse gas verification, management, and reporting by providing a structured approach to quantifying, reporting, and verifying these emissions. Introduced in 2006, it involved 175 global experts from 45 nations in a four-year development process. ISO 14064 was created in response to the growing need for standardised methods to manage climate-related impacts. It offers climate policy-neutral guidelines, meaning organisations can adopt these standards regardless of their country’s specific climate policies.
The primary objective of ISO 14064 is to help organisations accurately measure their GHG emissions and provide a framework for independent verification. By doing so, it guarantees the reliability of a company’s data to inform its sustainability strategies and report its environmental impact. The standard also supports policymakers by offering best practices for creating effective GHG reduction programs. It is particularly valuable for organisations participating in carbon markets or striving to achieve net zero emissions. And with the increasing pressure from stakeholders, regulators, and consumers to improve company sustainability practices and reduce carbon footprint, adhering to ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) principles and accurate and credible GHG accounting are strongly encouraged.
ISO stands for the International Organization for Standardization. It is a globally recognised, non-governmental organisation that develops voluntary international standards across various industries. Established to promote consistency and quality in products, services, and systems, ISO facilitates global trade by guaranteeing products and services meet international benchmarks. With over 25,000 standards, ISO covers quality management, environmental, and more. The ISO 14064 standard is one of its several environmental management standards.
What are the ISO 14064 standards?
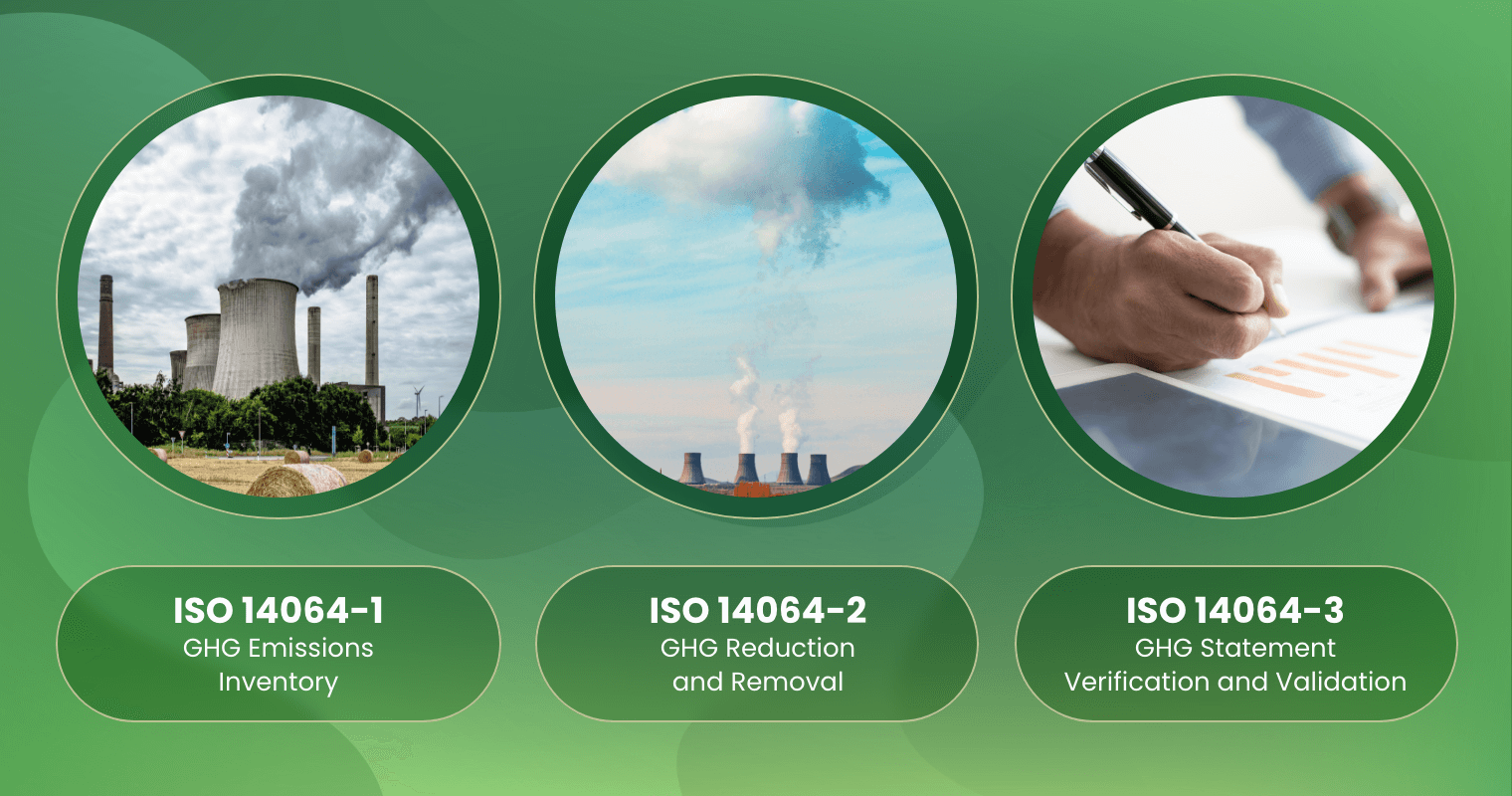
The ISO 14064 series consists of three parts, each focusing on a different aspect of greenhouse gas management.
ISO 14064-1: GHG Emissions Inventory at the Organisational Level
This section outlines how organisations can measure and report their GHG emissions through a bottom-up approach. It gives a guide on establishing the scope of their GHG inventory by setting the organisational and operational boundaries and the direct and indirect emissions, making sure reporting across different industries is consistent and accurate. The output then includes details on the boundaries, emissions by category, and the methodologies used to calculate them.
The six categories include:
- Category 1 covers direct emissions and removals from company activities, such as burning fuel or operational processes it controls.
- Category 2 includes indirect emissions from energy imported, like electricity, heat, or steam, produced elsewhere.
- Category 3 refers to indirect emissions from transportation, including emissions from vehicles and freight.
- Category 4 involves indirect emissions from products used by the company, such as raw materials or office supplies bought from external suppliers.
- Category 5 captures indirect emissions from the use of the company’s products, like energy consumed by customers when using the company’s goods or services.
- Category 6 includes indirect emissions from all other sources
ISO 14064-2: GHG Reduction and Removal Projects
This part accounts for and calculates GHG reduction and removal activities by the organisation. It focuses separately on emission reduction initiatives rather than the entire organisational GHG inventory. Companies can use this section to make sure their projects or technological improvements are achieving measurable environmental benefits.
ISO 14064-3: Verification and Validation of GHG Statements
This section is for the guidelines to validate and verify GHG data by external parties or internal auditors. It establishes principles for conducting independent audits, involving factors such as objectives, scope, and materiality, to guarantee the accuracy and reliability of the reports. This greenhouse gas verification increases the credibility of the data presented to stakeholders.
How to achieve ISO 14064 certification?
To achieve ISO 14064 certification, organisations must follow a structured approach that ensures the proper management, quantification, and reporting of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Here is the rundown of the process:
- Develop a comprehensive GHG inventory: Begin by identifying all sources of GHG emissions within the organisation’s operational boundaries. For direct emissions, consider sources like fuel combustion in company-owned vehicles or on-site heating systems. Indirect emissions might include electricity purchased from utility providers or emissions from outsourced activities. Including the emissions removed from specific emission reduction solutions or technology also add to the overall inventory. This allows for a comprehensive approach to GHG accounting and helps organisations capture the full scope of their emissions footprint and account for it.
- Establish clear reporting procedures: Set up consistent reporting mechanisms to document emissions accurately and conform to the details of all parts of ISO 14064. Include detailed explanations of the organisational boundaries, data collection methods, and any exclusions. Consistency and transparency are crucial in maintaining credibility and compliance with the standard.
- Conduct internal audits: Perform regular internal audits to verify the accuracy and completeness of the GHG inventory. Using standardised auditing procedures can level up the reliability of these assessments and help guarantee compliance with ISO 14064 certification requirements. This helps identify discrepancies with the data while aligning with ISO 14064 requirements before seeking external verification.
- Engage an independent verifier: Once the internal processes are refined, hire a third-party verifier to assess the GHG inventory against ISO 14064 standards. The verifier will evaluate the inventory’s consistency, accuracy, and compliance with established principles.
- Implement continuous improvement: After achieving certification, regularly review and update the GHG inventory to reflect changes in operations or reporting practices. Continuous improvement ensures ongoing compliance and enhances the organisation’s environmental performance.
What are the key benefits of ISO 14064 certification for companies?
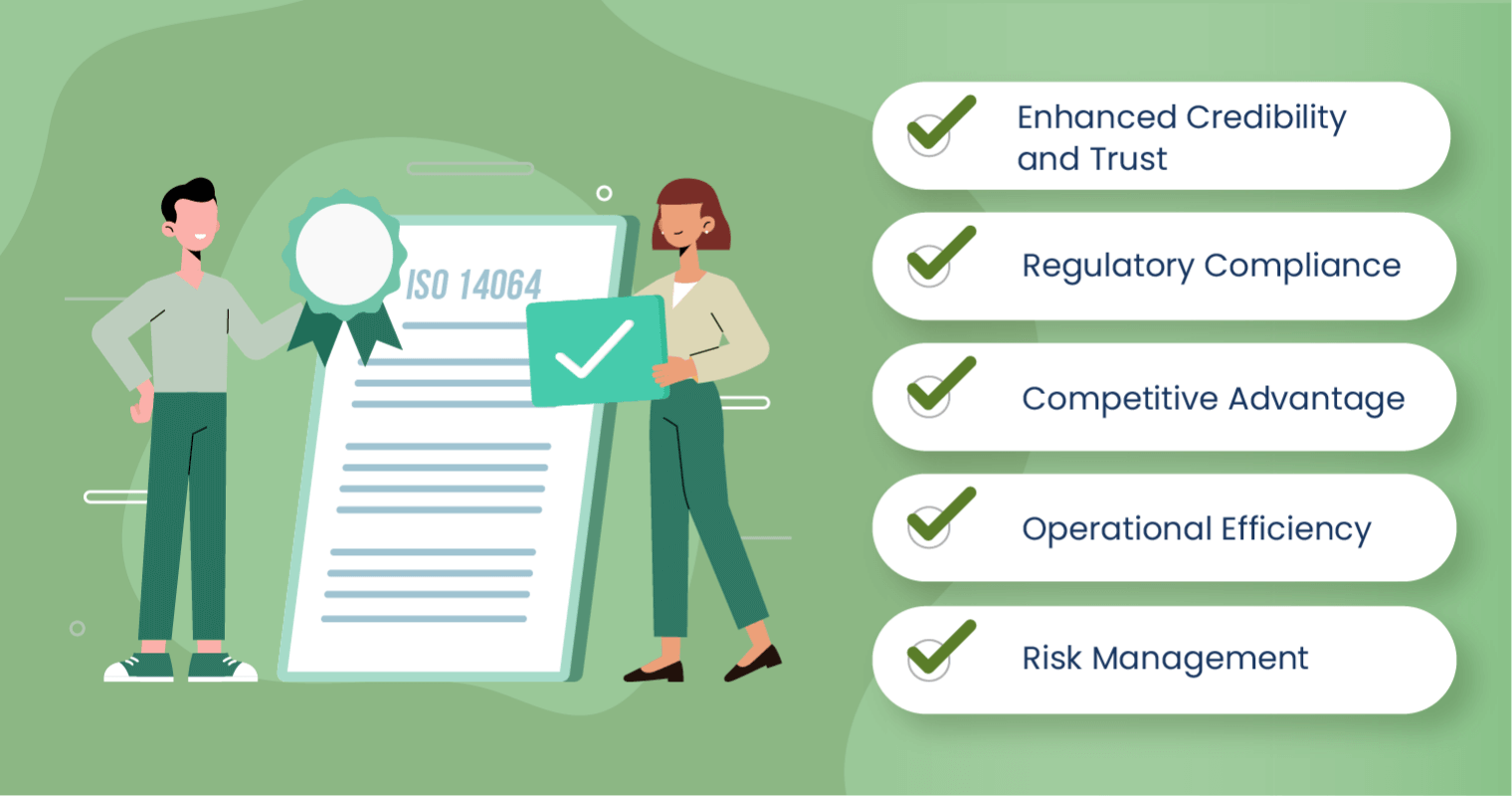
Listed are some key factors that can benefit your company:
- Enhanced Credibility and Trust: Certification demonstrates that a company’s GHG inventory and reporting processes meet international standards. This builds trust with investors, customers, and other stakeholders by showing a genuine commitment to sustainability. Organisations with credible reports are more likely to be perceived as reliable and responsible, which strengthens their reputation in the market.
- Regulatory Compliance: ISO 14064 helps companies meet legal requirements related to GHG reporting and reduction. It simplifies the process of complying with local, national, and international regulations on emissions. By adhering to a recognised framework, companies can avoid penalties and reduce regulatory risks.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses with ISO 14064 certification can differentiate themselves in the market by showcasing their commitment to environmental responsibility. Consumers and investors increasingly prefer environmentally conscious companies, and ISO certification can make businesses more attractive to these stakeholders.
- Operational Efficiency: By identifying sources of emissions, companies can optimise their operations to reduce waste and improve efficiency. This can lead to cost savings through better resource management, energy efficiency, and process improvements. Reducing emissions often goes hand in hand with cutting unnecessary expenses.
- Risk Management: The standard provides a systematic approach to managing climate-related risks. These risks include regulatory changes, reputational damage, and physical risks from climate change, such as extreme weather events. Implementing ISO 14064 can help companies proactively address these risks and improve their resilience.
ISO 14064 vs. GHG Protocol vs. Bilan Carbone
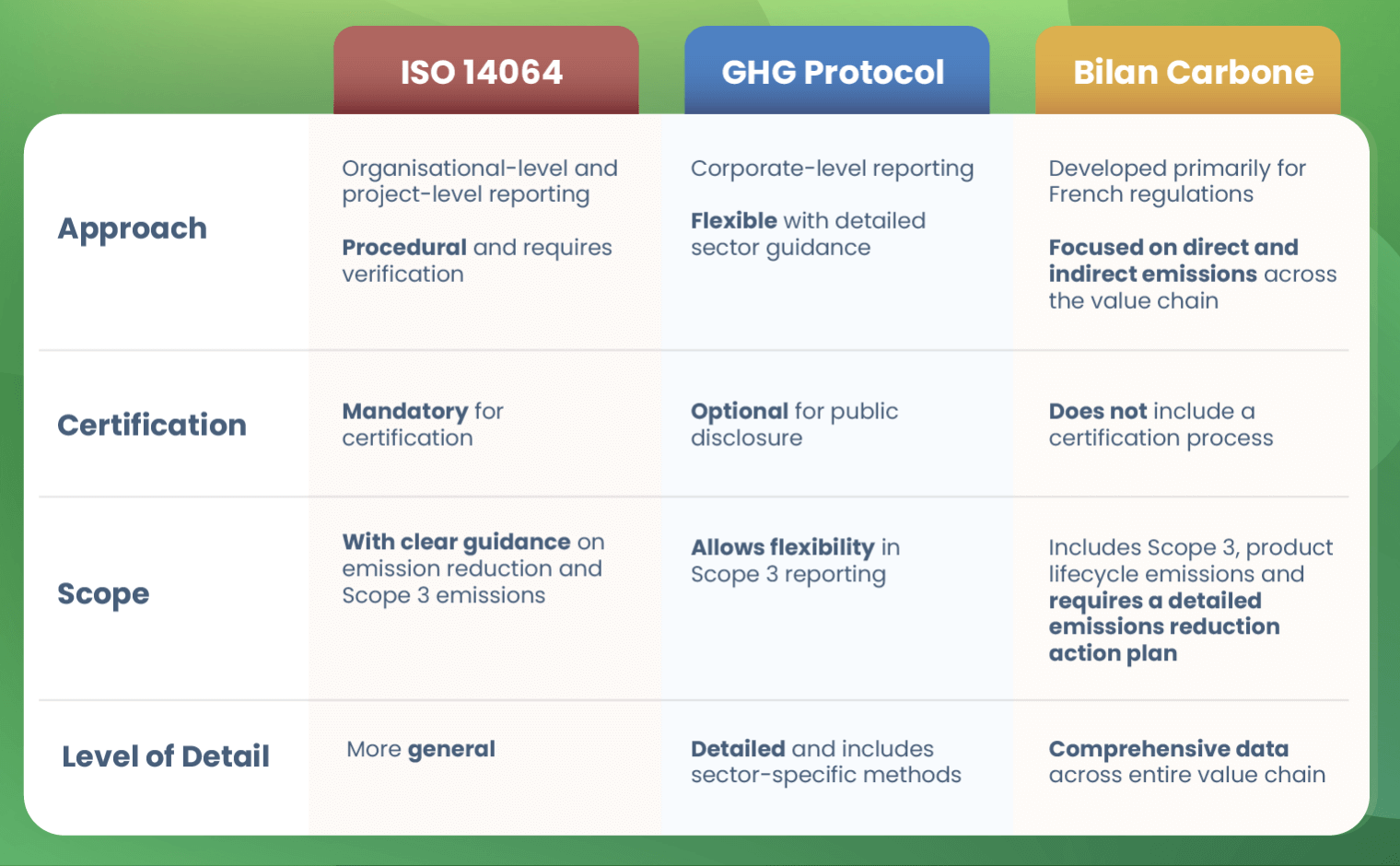
ISO 14064, GHG Protocol, and Bilan Carbone are three recognised frameworks for quantifying and reporting greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, but they differ in several significant ways— approach, verification, scope, and level of detail.
Approach and Verification
ISO 14064 offers a more procedural approach, providing a structured process for GHG quantification, reporting, and verification. It includes requirements for third-party verification, making it ideal for organisations seeking formal certification. The framework applies both to organisational-level reporting and specific project-level emissions reductions, classifying emissions into six categories.
In contrast, the GHG Protocol is more flexible and provides detailed guidance on calculating emissions for various activities and sectors. It is especially useful for corporate-level reporting, offering comprehensive methods for determining Scope 1, Scope 2, and Scope 3 emissions. However, it does not mandate third-party verification.
As for Bilan Carbone, it was developed by the French Environment and Energy Management Agency (ADEME) and includes both direct and indirect emissions across the entire value chain, requiring a detailed action plan for emissions reductions. Unlike ISO 14064 and GHG Protocol which are already globally used, Bilan Carbone is adapted to French regulations but can also be adapted outside France.
Scope and Level of Detail
A key distinction is that the GHG Protocol focuses more on corporate-level reporting and includes detailed sector-specific guidance and calculations associated with the entire corporation. This makes it highly useful for businesses needing extensive resources to understand their emissions. ISO 14064, however, takes a broader approach, focusing more on principles and less on prescriptive methods for quantifying greenhouse gases at their organisational level and project-level reporting. ISO 14064 and Bilan Carbone also address emissions, removals, and product lifecycle emissions, whereas the GHG Protocol is less clear on these topics but allows for their reporting separately. Lastly, ISO 14064 has clearer guidance on Scope 3 emissions, whereas the GHG Protocol leaves room for interpretation regarding these indirect emissions.
What are the applications of ISO 14064?
ISO 14064 is widely applicable across different sectors. Its primary applications include:
- Sustainability Reporting: Companies integrate ISO 14064 into their sustainability or ESG reporting to demonstrate transparency and accountability in their environmental impact. By following this standard, organisations can present more credible and accurate GHG emissions reporting to their stakeholders.
- Corporate GHG Inventories: Organisations use the standard to create comprehensive and verifiable GHG inventories. This ensures consistent reporting across industries, allowing businesses to track their progress toward emission reduction goals and identify key areas for improvement.
- Internal Auditing: Companies use the verification process outlined in Part 3 to conduct internal audits of their GHG accounting and inventories. This ensures continuous improvement, compliance with best practices, and readiness for external verification when needed.
- Carbon Markets: An ISO 14064 standard helps businesses participate in carbon trading by providing a reliable framework for verifying emissions reductions. It ensures that companies can trade carbon credits with confidence, knowing their reductions have been independently verified.
- Policy Development: Governments and regulatory bodies use the standard to create policies and programs aimed at reducing national GHG emissions. ISO 14064 provides a consistent methodology that can be adapted to various policy frameworks.
- Project Management: The standard supports the management of specific emission reduction projects, helping organisations achieve environmental goals and targets. It provides guidance on setting clear objectives, measuring progress, and verifying results to maximise the impact of these projects.
What are common challenges in ISO 14064 implementation?
Implementing ISO 14064 can be challenging due to technical, organisational, and resource-related issues, particularly in data consistency across various systems and formats and adopting specific software tools. Here are several crucial points to consider:
- Data Collection and Accuracy: One of the main challenges is gathering accurate and complete data across various sources. organisations may struggle with inconsistent data formats, incomplete records, or outdated information, which can compromise the integrity of the GHG inventory.
- Defining Boundaries: Establishing clear organisational and operational boundaries can be complex, especially for companies with multiple facilities or joint ventures. It helps to determine which emissions sources should be included and whether to use a control-based or equity-share approach. The control-based approach includes emissions from operations over which an organisation has financial or operational control, while the equity share approach accounts for emissions based on the organisation’s share of ownership in the operation.
- Resource Allocation: Implementing ISO 14064 requires dedicated resources and investments towards sustainability. This includes time, manpower, and finances that are involved in the continuous ISO 14064 carbon footprint accounting and environmental sustainability improvement. Smaller companies may face difficulties allocating these resources, which can slow down the certification process.
- Internal Knowledge and Training: Lack of understanding and involvement among employees and stakeholders about the importance of GHG reporting can be a roadblock to implementation. To address this, organisations should consider implementing targeted training or educational programs, such as workshops on GHG protocols, online courses or refreshers on sustainability practices, to keep those involved updated on the latest standards. These initiatives can help build a culture of accountability and reinforce the significance of accurate reporting.
What is the future outlook for ISO 14064?
The demand for ISO 14064 certification is expected to grow as businesses and governments intensify their focus on sustainability and net zero goals for 2050. With increasing regulatory pressures and stakeholder expectations, more organisations will turn to ISO 14064 to demonstrate credible GHG management practices. The standard is also likely to evolve to incorporate new developments in climate science and GHG accounting methodologies. As industries continue to innovate, ISO 14064 will play its role in harmonising GHG reporting frameworks globally. In the future, companies with certified GHG inventories may gain competitive advantages, such as better access to green financing and improved brand reputation. Moreover, as climate risks become more prominent, the standard will serve as a valuable tool for organisations to manage and reduce their carbon footprint effectively.
FAQs about ISO 14064 and GHG verification
1. Is ISO 14064 and GHG Protocol certifiable?
ISO 14064 can be certified through a third-party verification process, but the GHG Protocol itself is not certifiable. The GHG Protocol provides guidelines for GHG accounting, while ISO 14064 offers a certifiable framework.
2. Can ISO 14064 incorporate other GHG frameworks?
Yes, ISO 14064 is flexible and can be integrated with other GHG frameworks. It aligns with various international GHG accounting methods, including the GHG Protocol and carbon trading systems, allowing organisations to streamline compliance with multiple reporting requirements simultaneously. This adaptability ensures that businesses can respond effectively to evolving climate policies and stakeholder expectations.
3. Why is GHG verification essential for businesses?
GHG verification ensures that a company’s reported emissions data is accurate, consistent, and credible. This verification builds trust with stakeholders, reduces the risk of misleading reports, and enhances the organisation’s environmental accountability.
4. How can my company start the ISO 14064 GHG verification process?
To begin the verification process, companies should first conduct a thorough internal review. Once ready, they can engage an accredited third-party verifier to assess the inventory and make sure it meets ISO 14064 requirements.
5. What are the costs and timeframes to get ISO 14064 certified?
The costs and timeframes for ISO 14064 certification vary depending on the organisation’s size, complexity, and readiness. Typically, the process can take several months and requires investment in data collection, internal audits, and third-party verification fees.
Stay Ahead of ESG Compliance with Convene ESG
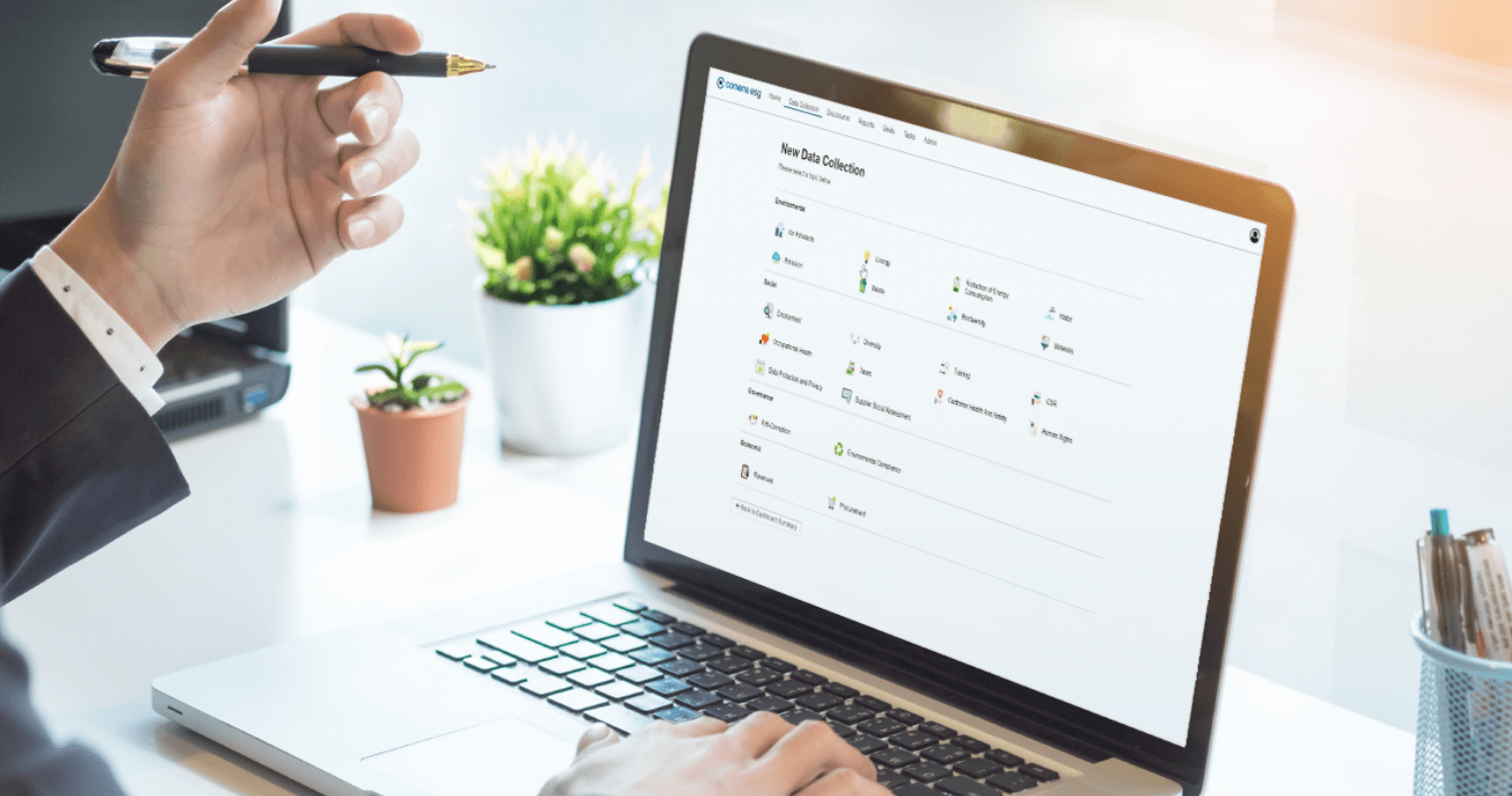
Many organisations struggle with the technical and resource-related aspects of implementing ISO 14064 standards. Collecting accurate data, defining organisational boundaries, and conducting thorough internal audits can be time-consuming and difficult to manage. To address these challenges, ESG reporting software and platforms can provide significant support, offering streamlined solutions for tracking emissions, compiling reports, and ensuring adherence to global standards such as ISO 14064 .
Convene ESG is an example of a powerful ESG software that supports companies in achieving ISO 14064 certification. It offers features that make GHG inventory management, emissions tracking, and verification more efficient. Convene ESG integrates various frameworks for ESG reporting, including GHG Protocol and Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), allowing businesses to align their reports with multiple standards. Companies can simplify the complexities of GHG accounting and reporting, refine their overall environmental footprint assessments, and secure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Ready to level up your sustainability reporting and achieve ISO 14064 certification? Explore the capabilities of Convene ESG by booking a demo today.