With the escalating expectations of sustainability among companies, more investors are looking into high-quality ESG reporting with accurate, complete, and verified information. Their disclosures are expected to cover issues regarding climate risks, materiality, and board governance. Moreover, there is additional pressure from regulating bodies that mandate local requirements aligned with various global sustainability standards.
On June 22, 2022, Convene sponsored a significant panel discussion at the ESG Summit by Trueventus, titled “Smart Reporting: Leveraging on Digital Solutions for Quality and Efficient ESG Reporting.” This session underscored Convene’s deep commitment to advancing ESG practices in the ASEAN region, addressing the challenges and technological advancements shaping ESG reporting. The panel featured experts including Katherine Pamintuan, ESG Manager at Convene ESG; Lawrence Loh, Director of the Centre for Governance and Sustainability at NUS Business School; Phang Oy Cheng, Head of Sustainability Advisory Services at KPMG Malaysia; and Shih Hor Lau, CEO and Co-Founder of Elixir Technology Pte Ltd. Moderated by Syahrir Suib, Business Development Executive at Convene Malaysia, the discussion explored how companies can report on ESG effectively and accurately, meeting the demands from both investors and regulators.

Understanding ESG & Sustainability Reporting in Malaysia
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors have become crucial benchmarks for assessing corporate responsibility and sustainability in Malaysia. As companies face growing scrutiny from investors, regulators, and consumers, they are increasingly adopting ESG company frameworks to demonstrate their long-term commitment to ethical business practices and sustainable growth.
In Malaysia, Bursa Malaysia’s Sustainability Reporting Guide plays a pivotal role in shaping the way companies report on ESG issues. This guide, updated in 2022, provides clear guidelines on how companies should disclose their environmental, social, and governance impacts. It encourages businesses to align with both local and international standards while addressing Malaysia’s unique sustainability challenges.
Environmental Considerations
Malaysia faces significant environmental challenges, including deforestation, biodiversity loss, and the effects of climate change. Bursa Malaysia’s Sustainability Reporting Guide mandates companies to disclose their environmental impact through indicators such as carbon emissions, energy efficiency, water use, and waste management. These disclosures are not merely check-the-box exercises but are designed to align with the nation’s broader sustainability goals, such as the Malaysia Climate Change Action Plan and the MyHijau Programme, which promote renewable energy and green technologies.
The guide also emphasises the importance of addressing environmental risks specific to Malaysia, such as palm oil production and land degradation. By reporting on these critical issues, companies demonstrate how they contribute to national and global environmental objectives.
Social Impact and Labour Practices
Regarding social responsibility, the guide stresses the need for companies to report on ethical labour practices, workforce diversity, human rights, and their engagement with local communities. In Malaysia, where issues like labour rights and social equity remain critical, ESG reporting has pushed companies to focus on improving working conditions and reducing inequality.
Bursa Malaysia requires detailed disclosures on how businesses are contributing to social initiatives, particularly those aligned with the country’s Shared Prosperity Vision 2030. This ensures that ESG reporting reflects the real social impact of companies, from labour practices to community development, and highlights their role in driving inclusive growth within the country.
Governance and Accountability
Corporate governance in Malaysia has historically been a key area of focus, especially with ongoing efforts to combat corruption and promote transparency. Under Bursa Malaysia’s Sustainability Reporting Guide, governance reporting is highly emphasised, requiring companies to disclose board diversity, executive pay structures, and anti-corruption measures.
Malaysian companies must adhere to the Malaysian Code on Corporate Governance (MCCG), which sets a high bar for ethical business conduct and transparency. ESG reporting under Bursa Malaysia ensures that companies maintain strong governance frameworks, helping them manage risks while fostering trust among stakeholders.
Materiality and Stakeholder Engagement
A critical aspect of Bursa Malaysia’s approach to ESG reporting is its emphasis on materiality. Companies are expected to conduct materiality assessments to identify the ESG issues that are most relevant to their business and stakeholders. This ensures that reports focus on the most significant environmental, social, and governance risks, rather than generic disclosures.
Moreover, the guide encourages robust stakeholder engagement. This means companies must actively involve investors, employees, regulators, and communities in their ESG strategy, aligning their practices with stakeholder expectations.
Aligning with Global Standards
While Bursa Malaysia’s Sustainability Reporting Guide is designed for local relevance, it is also aligned with international frameworks such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), and Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). This ensures that Malaysian companies are not only compliant with local regulations but are also able to meet global investor expectations for transparency and sustainability.
It is important to note that, while ESG reporting is not fully mandatory, several key initiatives and frameworks have been established to guide companies:
- The Malaysian Code on Corporate Governance: The MCCG promotes good corporate governance practices, encouraging companies to integrate ESG Malaysia factors into their reporting. While adherence to governance standards is voluntary, companies listed on the Bursa Malaysia are encouraged to disclose their ESG initiatives to align with the code.
- The Sustainable and Responsible Investment (SRI) Framework: Malaysia has introduced the SRI framework to support companies focused on sustainability and responsible investing. This framework encourages businesses to issue ESG reports and demonstrates the country’s commitment to aligning with global sustainability standards.
- The ESG Index Series: Launched by Bursa Malaysia, the ESG Index Series provides a benchmark for companies excelling in ESG performance. Companies listed in this index are recognised for their commitment to ESG best practices and adherence to the Malaysia ESG framework. While inclusion in the index is not mandatory, it signals a company’s leadership in the realm of sustainability and ESG reporting.
The Importance of ESG Reporting for Malaysian Companies
The growing emphasis on ESG reporting highlights its importance for companies aiming to meet stakeholder expectations and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving business landscape. Companies in Malaysia that adopt robust ESG reporting practices can benefit in several key ways:
- Build trust and confidence of stakeholders: Transparent ESG disclosure fosters trust among investors, customers, and regulators. By communicating how the company addresses key ESG risks and opportunities, organisations build long-term confidence in their business strategies.
- Enhance market performance and competitive advantage: Companies that perform well on ESG metrics often see improved market performance. Strong ESG practices can lead to better financial outcomes, attract socially conscious investors, and enhance the company’s reputation in the market.
- Contribute to global initiatives to combat climate change: By adopting effective ESG sustainability Malaysia initiatives, companies can actively contribute to global efforts to combat climate change and reduce carbon footprints. Organisations that prioritise environmental goals align themselves with international climate action frameworks, further solidifying their market position.

The Challenges in ESG Reporting in Malaysia
Most companies see ESG reporting as a once-a-year one-off exercise — looking at the report as the ultimate goal of their sustainability initiatives. Hence, throughout the year, ESG data is a low priority of the company leaders. The challenge then lies in the tedious annual data collection.
In the same panel discussion, Katherine Pamintuan, ESG Manager at Convene ESG, mentioned the four pain points in ESG reporting, namely:
- The struggle in gathering missing data
- Uncertainty in data accuracy
- Limited visibility of trends and benchmarking
- Constant changes in disclosure requirements
Without proper governance of sustainability initiatives and disclosures, these challenges may recur and affect the brand’s reputation.
As Phang puts it, “If you collect the wrong data and source, you increase your chance of misstatements in your public report. That is the biggest challenge.”
In the ASEAN market, the same pain points transpire according to a recent study conducted by Lawrence Loh, Director of the Centre for Governance and Sustainability at NUS Business School, and his team at NUS. The conceptual framework they used has incorporated two factors on sustainability practices — the ESG principles, which cover stakeholder engagement, materiality, and the like, and the content of the ESG report, covering sustainability performance, targets, and framework.
Their findings show that most companies in the region, especially last year, adhere to presenting a sustainability report subsuming general ESG principles. “But in terms of the specifics of the report, performance, and reporting frameworks, they came up a little bit weaker. The specific manifestation of ESG still needs to improve,” Lawrence concluded. Thus, there is a call for leaders and boards to take on their responsibilities of educating themselves about ESG to improve the journey.
Another challenge in ESG reporting is the lack of understanding of the data. Most corporations still see sustainability reports or statements as a compliance requirement instead of an operational approach. “The whole idea behind [reports] is to make sure you can measure your progress and how to get to your goals,” Shih Hor Lau, CEO and Co-Founder of Elixir Technology Pte Ltd, said. By not taking a deep-rooted process approach, companies may only end up with data weakness and misstatements.
Leaders must also understand the correlation between the company’s financial information and the ESG data. Knowing how one affects the other can improve data collection, validation, and tracking — taking the same rigour with sustainability data as to how companies do with financial data.
Best Practices of ESG Reporting for Malaysian Companies
Effective ESG reporting involves several best practices to ensure comprehensive, transparent, and actionable disclosures. Adhering to these practices helps companies meet regulatory requirements, build stakeholder trust, and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
- Define Purpose and Scope: Clearly defining the purpose and scope of ESG reporting is crucial. Companies should identify the key ESG issues that are relevant to their operations and stakeholders. This involves setting specific goals, determining the scope of reporting, and aligning with relevant ESG reporting standards. A well-defined scope helps ensure that the report addresses the most significant ESG impacts and risks.
- Engage Stakeholders: Engaging with stakeholders, including investors, employees, and community members, is a critical component of effective ESG reporting. Companies should seek input from these groups to understand their concerns and expectations regarding ESG issues. This engagement helps in prioritising the most relevant ESG topics and ensures that the reporting addresses the needs of all key stakeholders.
- Collect and Manage Data: Accurate and reliable data collection is essential for credible ESG reporting. Companies should establish robust systems for gathering, managing, and verifying ESG data. This includes implementing tools such as sustainability reporting software and ESG reporting software to streamline data management and ensure consistency across reports.
- Report and Enhance: Once the data is collected from sustainability software, companies should prepare their ESG reports in accordance with established ESG reporting standards. The reports should be clear, comprehensive, and accessible to stakeholders. After reporting, companies should seek feedback and continuously enhance their ESG practices and reporting processes to address emerging trends and improve transparency.

ESG Reporting Support and Resources for SMEs in Malaysia
SMEs in Malaysia face unique challenges in ESG reporting due to limited resources and expertise. To address this, several initiatives are available to support them in integrating ESG practices.
- Simplified ESG Disclosure Guides: Bursa Malaysia, SME Corp, and other industry bodies provide simplified ESG reporting guides tailored to SMEs. These resources break down complex requirements into practical steps, helping small businesses meet compliance standards without overwhelming them.
- Capacity-Building Programs: Government agencies such as SME Corp and the Malaysia Green Technology Corporation (MGTC) offer training and workshops to enhance SME understanding of ESG. These programs cover key areas like sustainability reporting, environmental management, and social responsibility, enabling SMEs to align with Malaysia’s ESG frameworks.
- Financial and Technical Assistance: SMEs can access financial support through schemes like the Green Technology Financing Scheme (GTFS) and Green Investment Tax Allowance (GITA). These help offset the costs of adopting ESG software and implementing sustainable practices.
By leveraging these resources, Malaysian SMEs can improve their ESG performance, aligning with national sustainability goals while enhancing their competitiveness in both local and international markets.
2024 and beyond: ESG Reporting Trends in Malaysia
The landscape of ESG reporting in Malaysia is evolving rapidly, with several specific trends shaping how companies approach sustainability and transparency.
- Regulatory Emphasis on ESG Compliance: Malaysia’s regulatory bodies, particularly Bursa Malaysia, are increasingly focused on ESG compliance. The Bursa Malaysia Sustainability Reporting Guide requires companies listed on the exchange to disclose their ESG performance, driving more comprehensive and transparent reporting. Additionally, initiatives like the MCCG emphasise strong governance and climate risk management, pushing companies to meet stricter ESG standards.
- Integration of ESG into Corporate Strategies: Malaysian companies are progressively embedding ESG considerations into their core business models. With regulatory pressure and the growing importance of sustainable investments, large corporations and SMEs alike are aligning their business strategies with ESG goals to ensure long-term resilience and value creation. The Securities Commission Malaysia’s SRI Sukuk framework further supports businesses in incorporating ESG into their financial strategies.
- Adoption of ESG Reporting Software: The adoption of ESG reporting software is becoming common in Malaysia, driven by the need for more efficient data management and reporting processes. Tools like the Bursa Malaysia Sustainability Toolkits help companies streamline data collection, automate compliance, and meet local ESG reporting requirements.
- Climate Risk Disclosure: Malaysian companies, particularly in sectors like finance, energy, and agriculture, are increasingly focusing on disclosing climate-related risks. This aligns with global frameworks like the TCFD, which Bursa Malaysia encourages companies to adopt.
- Stakeholder Engagement and Transparency: There is a growing trend among Malaysian companies to enhance engagement with stakeholders on ESG issues. This is not only driven by regulatory requirements but also by a need to build trust with investors, customers, and local communities. As part of this, companies are making more efforts to integrate Malaysia’s ESG goals with community and investor expectations.
The Role of Digitalisation in Sustainability and ESG Reporting
One of the trends mentioned in ESG reporting is the use of digital software to streamline operations while upholding data accuracy. Developing an accurate and verified ESG report plays a big role in your sustainability efforts, stakeholder management, and reputation. Having incomplete and inaccurate data on your sustainability reports can only harm your organisation. Thus, with these challenges in data collection and assurance, this is where technology comes in and addresses the gaps.
The role of digitalisation in ESG reporting can be summarised into four imperatives: Automate, Validate, Mitigate, and Navigate.

With digitalisation, all the data can be collected, inputted, and managed in one place while complying with reporting standards or frameworks — eliminating the manual processes. Moreover, it allows organisations to prove all the information and track goals to take corrective actions as needed.
An ESG reporting software is an ideal manifestation of digitising the reports. The automated process of data collection and the customisability of the system make it an efficient reporting tool. In selecting the best ESG technology for your organisation, Katherine also pointed out technical factors to consider for your evaluation.
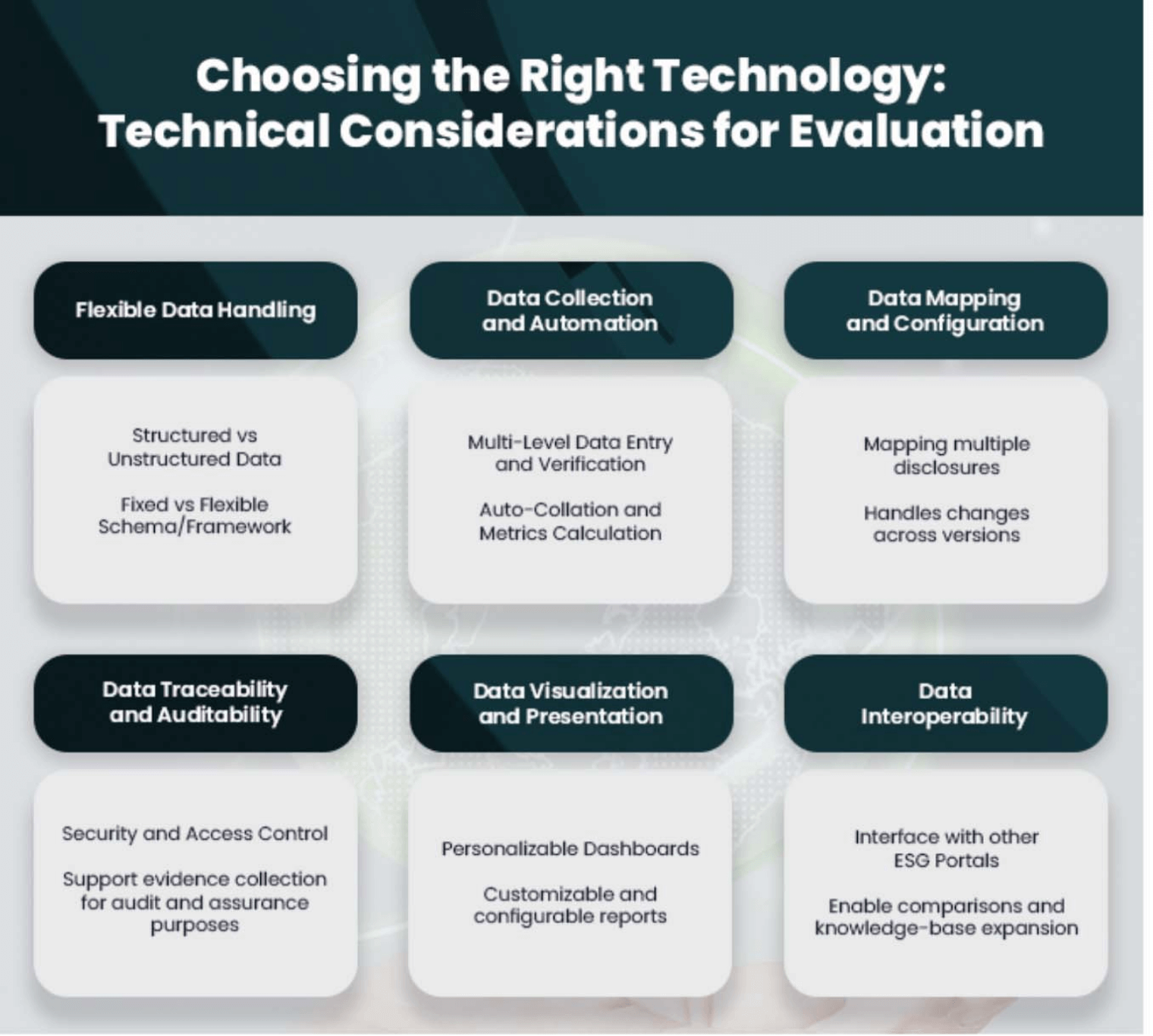
“Through digitisation and digitalisation, we can now enable ownership and accountability in all the workflows, because after all, ESG is not a one-man job. There should be ownership not just from one person or one team but across the entire organisation,” Katherine remarked.
Implement Sustainability Reporting Software for Smarter Disclosure
Convene ESG stands at the forefront of ESG reporting in Malaysia, offering a comprehensive solution designed to digitise your sustainability data and align it with both local and global standards.
Our ESG reporting software provides best-practice recommendations for disclosures and features customizable performance dashboards to analyse trends and benchmark against industry peers. The automatic generation of reports helps create compelling narratives tailored to your stakeholders’ needs.
Learn more about how Convene ESG can help you with sustainability reporting. Request a demo now!














